| [n] |
[na] |
/na/ |
`borrow’ |
| |
[nha] |
/nha/ |
`close
(dish only)’ |
| |
[no] |
/no/ |
`you’ |
| |
[nu] |
/nu/ |
`laugh’ |
| |
[nhu] |
/nhu/ |
`to
pull out from the root’ |
| |
[^>na] |
/ana/ |
`cooked
rice’ |
| |
[^nha] |
/anha/ |
`mucus’ |
| |
[^nu] |
/anu/ |
`child’ |
| |
[^nhu] |
/anhu/ |
`artiery’ |
|
|
| /n/.
It is an unaspirated voiced velar nasal. Unlike the other nasals in
the Sema. /*/, does not have an aspirated counterpart even at the
phonetic level. It does not have any positional variant either. This
phoneme has a defective distribution in that, it does not occur before
front vowels and in the word-final position. Given below are a few
words illustrating the occurrence of this phoneme. |
| [´] |
[ o] o] |
/ o/ o/ |
`rest, stop’ |
|
[ nosali] nosali] |
/ osali/ osali/ |
`sugar’ |
|
[ uvi] uvi] |
/ uwi/ uwi/ |
`health’ |
|
[^ńi´u] |
/ani u/ u/ |
`hyena’ |
|
[pu u] u] |
/pu u/ u/ |
`five’ |
|
[a^> 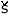 ś] ś] |
/a sś/ sś/ |
`tiger’ |
|
[a^ a] a] |
/a a/ a/ |
`daughter’ |
|
|
| Unvoiced
Fricatives |
| The
unvoiced fricatives in Sema show a four-way opposition in the place
of articulation. These are labio-dental, dental, velar and glottal.
For the sake of pattern congruity, the labiodental fricative is placed
in the place of the bilabial. Given below is a description of individual
unvoiced fricatives. |
| /f/
is an voiced labio-dental fricative. It occurs only before the back
vowels. The language has also a voiced labiodental phone with slight
friction. It occurs before the front and the central vowels. Since
[f] and [v] are in complementary distribution, the two could have
been grouped together to form a single labio-dental fricative. This,
however, is not done because (i) [v] is in multiple complementation
with [f] and [w] and hence could be grouped with either of them and
(ii) out of the consideration for the strong views of the Sema community
who are very particular in retaining f as a distinct is grouped with
/w/ and /f/ is given phonemic status. (For the grouping of [v] with
[w], please refer p.319. |
| /f/.
It does not have any perceptible positional variant. The functional
load of this phoneme is extremely low. It occurs in a very few words
in the entire vocabulary and that too only before back vowels. Given
below are a few words to illustrate the occurrence of this phoneme.
|
| [f] |
[fu] |
/fu/ |
`blow’ |
|
[fś] |
/fś/ |
`cook’ |
|
[fulo] |
/fulo/ |
`hook’ |
|
[^fo] |
/afo/ |
`elder sister’ |
|
[^fuko] |
/afuko/ |
`trumpet’ |
|
|
| /s/.
It is an unvoiced dental fricative. [s&], the palatal fricative
occurs before non-central vowels as a positional variant of this phoneme.
This phoneme does not occur in the word-final position. Given below
are a few words to illustrate the occurrence of the phoneme. |
[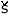 ] ] |
[s.gif) ] ] |
/so/ |
`hard’ |
|
[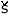 i] i] |
/si/ |
`do’ |
|
[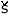 e] e] |
/se/ |
`praise’ |
|
[^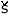 W W.gif) ] ] |
/aso/ |
`bread’ |
|
[^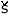 ś] ś] |
/asś/ |
`spike’ |
|
[^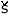 e] e] |
/ase/ |
`margin’ |
| [s] |
[sa] |
/sa/ |
`sector’ |
|
[s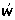 ] ] |
/s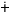 / / |
`sickness’ |
|
[^s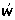 ] ] |
/as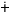 / / |
`wood’ |
|
[ms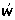 ] ] |
/ms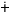 / / |
`suck’ |
|
[^są] |
/asą/ |
`hair’ |
|
[^sį] |
/asį/ |
`cooked meat’ |
|
|
| /x/.
It is an unvoiced glottal fricative. It does not have any perceptible
positional variant. It does not occur in the word-final position.
given below are a few illustrative words showing the occurrence of
this phoneme. |
| [x] |
[xe] |
/xe/ |
`pounding’ |
|
[xW] |
/xo/ |
`pluck’ |
|
[xu] |
/xu/ |
`slow’ |
|
[^xu] |
/axu/ |
`rafter’ |
|
[^xa] |
/axa/ |
`crop’ |
|
[^xi] |
/axi/ |
`particles of paddy' |
|
|