| [^gili] |
/agili/ |
`partridge’ |
| [^guś] |
/aguś/ |
`a
bee’ |
|
|
| Affricates
|
| At
the phonemic level, Sema has only one affricate. It is the unvoiced
unaspirated dental one. It has also an aspirated counter-part. Just
as in the case of the aspirated stops, the aspirated affricate ia
also phonemic zed as a sequence of the unaspirated affricate and /h/.
Given below is a description of the affricate. |
| /c/.
It is an unvoiced unaspirated dentals affricate. It has two positional
variants, viz., [c] the dental affricate occurring before the central
vowels and [c&], the palatal affricate occurring elsewhere. This
phoneme does not occur in the word-final position. Given below are
a few illustrative words showing the occurrence of this phoneme. |
| [c] |
[c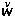 ] ] |
/c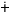 / / |
`decay’ |
| |
[ch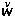 ] ] |
/ch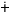 / / |
`ti’ |
| |
[cį] |
/cį/ |
`chew’ |
| |
[cha] |
/cha/ |
`any
object with a good finishing' |
| |
[^c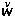 ] ] |
/ac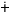 / / |
`dog’ |
| |
[^ch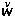 ] ] |
/ach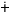 / / |
`a
thread ball’ |
| |
[^chamFa] |
/achamra/ |
`handicraft’ |
[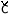 ] ] |
[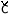 o] o] |
/co/ |
`support’ |
| |
[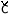 ho] ho] |
/cho/ |
`sweep’ |
| |
[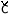 e] e] |
/ce/ |
`give
way’ |
| |
[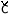 he] he] |
/che/ |
`hit’ |
| |
[^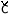 u] u] |
/acu/ |
`fodder’ |
| |
[^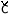 ila] ila] |
/acila/ |
`necklace’ |
|
|
| Nasals
|
| The
nasals in Sema show a three-way opposition at the place of articulation.
These are bilabial, dental and velar. Of these the bilabial and dental
nasals have both aspirated and unaspirated varieties. However, just
as in the case of the aspirated stops, the aspirated nasals are also
phonemic zed as the sequence of the concerned nasal and /h/. An important
feature to be noted about the aspirated nasals is that at the word-initial
position the entire sound occurs in a single chest pulse (phonetic
syllable) but at the word-medial position the nasal segment occurs
in one chest pulse and the aspiration occurs in the succeeding chest
pulse. Since chest pulse is not a phonemic unit, this feature of the
aspirated nasals is ignored here. Alternatively, the occurrence of
the aspirated nasals could be restricted only to the word-initial
position by treating the word-medial occurrences as the corresponding
nasal plus the glottal fricative. Since all the aspirated consonants
are segmented at the phonemic level as the concerned consonant plus
the glottal fricative, such an alternative treatment would not result
in any additional advantage. All nasals are voiced, but voicing is
not a relevant feature with the nasals. No nasal occurs at the word-final
position. Given below is a description of the individual nasal phonemes.
|
| /m/.
It is an unaspirated bilabial nasal. It does not have any perceptible
positional variant. It does not occur at the word-final position.
Given below are a few illustrative words showing the occurrence of
this phoneme. |
| [m] |
[me] |
/me/ |
`throat’ |
| |
[m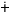 zµ
¸] zµ
¸] |
/m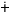 z z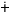 ¸/
¸/ |
`straight’ |
| |
[mo] |
/mo/ |
`no’ |
| |
[mhó] |
/mhó/ |
`dull
weather’ |
| |
[mi] |
/mi/ |
`ill
omen’ |
| |
[mhi] |
/mhi/ |
`clouded
sky’ |
| |
[^me] |
/ame/ |
`price’ |
| |
[^mhe] |
/amhe/ |
`capital’
(property)’ |
| |
[timģ] |
/timģ/ |
`man’ |
| |
[^ma] |
/ama/
|
`son-in-law’ |
|
|
| /n/.
It is an unaspirated dental nasal. Before a front vowel it has the
palatal variant, [ń]. This phoneme does not occur in the word-final
position. Given below are a few illustrative word showing the occurrence
of this phoneme. |
| [ń] |
[ńi] |
/ni/ |
`I/me’ |
| |
[ńhekobo] |
/nhekobo/ |
`banyan
tree’ |
| |
[ńhi] |
/nhi/ |
`marry
(girls)’ |
| |
[^ńe] |
/ane/ |
`goat’ |
| |
[^ńhč] |
/anhč/ |
`worn
out thing’ |
| |
[^ńhe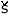 ś] ś] |
/anhesś/ |
`jealously’ |
| |
[^ńhipo] |
/anhipo/ |
`steep
rock’ |
|
|