| (a) Without
a marker: |
| Rule
: No change in the structure of the statement type sentence,
only the terminal pitch has to be raised. |
| Illustration |
bulu -ko
caba jana -ko
caba jana
|
‘the salt
has been finished’
|
bulu -ko
caba jana -ko
caba jana
|
‘has
the salt been finished?’
|
|
|
| Rule
: Suffix /ci/ in the end of the statement and raise
the terminal pitch to expect yes or no answer. |
|
or
|
|
Suffix /cika/
either in the end or before the
|
|
verb phrase,
in the latter case suffix the pronominal
|
|
subject to
it. The terminal pitch may be either
|
|
level or rising
or falling /cika/ also expresses doubt.
|
|
|
|
or
|
|
Place/ cina/
before the verb phrase along with
|
|
the pronominal
subject. Terminal pitch may be
|
|
any of the
three types
|
|
|
|
or
|
|
Place/ cia
/ with rising intonation in the beginning
|
|
of the sentence
as a separate clause. The main
|
|
sentence will
have rising tone in the end separately.
|
|
/cia/ is rather
used as a question voactive. Sometime
|
|
the question
marker /ci/ may additionally be used in
|
|
such compound
sentences.
|
|
|
| Illustrations |
bulu -ko
caba jana ci -ko
caba jana ci
|
|
‘has the salt
been finished?’
|
|
kimin-do sukuai-leka
menai cika /l/Æ
|
|
‘however,
is the bride lovely or not?’
|
rapud-jan-re
o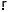 o?
cinam omaliNa
/l/Æ o?
cinam omaliNa
/l/Æ
|
|
‘if it breaks,
would you give us one?’
|
|
cia ho
dasinam ci
|
|
‘what my boy?
will you serve?’
|
cia
bulu -ko
caba-jana -ko
caba-jana
|
|
‘what? has
the salt been finished?’
|
|
|
| 4.3.1.
Interrogative type questions: |
| Such questions
are classified as interrogative type. There is a number of markers
to be used differntly for nominal, adjectivel and adverbial interrogatives
which are derived from demonstrative. Adverbail interrogatives construct
questions enquiring about time, place, manner or cause of an action.
List of interrogatives is already given in § 2. |
| Rules: |
|
1. Replace the
noun, adjectve oradverb
of the statement withappropriate
interrogative.
|
|
2. Raise the
terminal pitch to makeit
a question, However, this isnot
obligatory.
|
|
|
| Illustrations |
en ku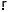 i-e
hiju? tana i-e
hiju? tana
|
‘that girl
is coming’
|
oko ku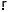 i-e
hiju tana /l/ i-e
hiju tana /l/
|
‘which girl
is coming?’ etc.’
|
|
|
| The particles ci,
cina, cia or other interrogatives may independently be used as questions: |
|
ciula?
|
‘when?’
|
|
cimta?
|
‘how?’
etc.
|
|
|
| 4.4.
Transformations for imperatives: |
| A
statement may be transformed into a command where it is made imperative
for the listener to give an action response. As such, the imperative
constructions are limited to the second person. The intonation. |