a Mao sentence), and depends upon a main clause to make good
sense. In the norm, subordinate clauses are protatic i.e., they
precede main clauses while main clauses are apodotic, they follow
subordinate clauses. |
6.4.2.1.
|
Subordinators |
|
Subordinators, the morpheme (sequence's which mark subordinate
clauses, could be either temporal ornontemporal. While temporal
subordinators have to do with the temporal relationship between
the verb phrases in the main clause and the subordinate clauses,
nontempral subordinators do not. Non-temporal subordinators may be
further sub-divided into (a) the quotative (b) the casual (c) the
disjunctive (d) the indirect question-introducer (e) the
conditional (f) the pseudo conditional/concessive, and (g) the
contingent. |
6.4.2.1.1.
|
Temporal Subordinators |
Genuine temporal subordinators seem to be only
three (a) v li v, where v stands for
verb which expresses the concept formalized in
English as ‘as soon as ; no sooner than...’ (b)
li/sa added to the nominalized form of
the verb which expresses the concept formalized
in English ‘as long as’ and (c) hie which
expresses the concept formalized in ‘when’. Other
temporal subordination is expressed by postpositions
added to the nominalized form of the verb.
|
a.
|
v li v. Two tokens of the same
verb straddling li denote that the action of the
main clause will take place about the time the
action of the subordinate clause terminates, that
the two actions constitute a continuum in time.
|
| 20
|
1. |
ai1
mikrüli2
lo-lo-lo3
ni-yi4
kade5
le6
|
| |
|
as soon
as3
I1
reach3
Imphal2
, I1
will6
meet5
you (sg.) 4 |
| |
|
|
| |
2. |
ni1
pfo2
he3
rü-li-rü4
khi vu5
le6
|
| |
|
(he) will6
return5 as soon
as/the moment4
you (sg.)1
write4
to3
him2
|
| |
|
|
| |
3. |
hihi1
to-li-to2
omüi3
thi-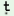 i
le4 i
le4
|
| |
|
people3
die4
as soon as2
(they) eat2
this1
|
|
b.
|
li/sa added to the gerundial form of
the verb denotes that the action of the main clause
will continue as long as the action of the subordinate
clause takes place, that the two actions will
be simultaneous.
|
| 21.
|
1. |
ni1
hrü-koco- { li }2
|
ai3
ni-yi4
koli pi5
le6
|
| |
|
{
sa } |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
I3
will6
look after5
you |
(sg.)4
as long as2
you (sg.)1
live2
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
2. |
ocü
irü-ko-o-(li)1
amazhi2
ho-e3
|
|
| |
|
as long
as there are/were |
rains, there
are/were no3
|
| |
|
|
problems/hassles
2 |
| |
|
|
|
| |
3. |
pfo1
iniu1
ko-bu (li)3
asa/covo bu-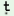 i-e4 i-e4
|
|
| |
|
he1
was happy4
as long |
as he was3
in the village1 |
|
c.
|
hie
added to the verb root denotes that the action
of the main clause takes place at the point of
time that the action of the subordinate clause
takes place.
|
| 22
|
1. |
ai1
pfo2
he3
vu hie4
pfo5
ayi6
prü-o7
cu ta-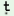 i-e8 i-e8
|
| |
|
when4
I1
went4
to3
him2
, he5
feared7
me6
and7
(he) ran away8
|
| |
|
|
| |
2. |
pfo1
ta2 vu-hie3
omüi-no4
ari-te5
|
| |
|
when3
he1
came3
, people4
made a lot of noise5
|
|
(d)
|
(i) cü, a word descriptive of time, added
to the participial form of the verb denotes that
the actions of the main and subordinate clauses
are at some point simultaneous, if not fully coterminous
:
|
|
23. |
1. |
ai1
hinahi2
mikrüli3
azhü ta-ko-o-cü(-no)4
phro-e5 |
|
|
I1
read 5
this2
while travelling 4
to Imphal 3 |
|
|
|
|
2. |
adani-no1
larücü2
-lino3
khi vu-ko-o cü4
hepuni-yi5 kade6
|
|
|
Adani1
met6
Hepuni5
when (he was) coming back4
from 3
school2
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
ai1
pfo2
nolu-koco cü-no3
ni-e4
|
|
|
I1
saw4
her 2 when
she was young2
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
ai1
bo-ko-o cü-no2
ni3
larü phro-lo4
|
|
|
while2
I1
cook2
, you3
study 4 |
|
|
|
|
5. |
omüi1
larü phro-ko-o-cü2
so kohu_)3
pi-sho4 |
|
|
don’t4
disturb3
when2
(somebody)1
studies2
|
|
|
(ii)
|
dzü(no)
‘before’ added to the negative participial form
of the verb denotes that the action of the main
clause precedes that of the subordinate clause
in time. |
|
24 |
1. |
ayi
peno1
ni2
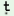 hu-ko-mo3
dzü-no4
odzü akhrü-o5 hu-ko-mo3
dzü-no4
odzü akhrü-o5 |
|
|
let
me1
wash-body parts5
before4
you(sg.)2
get up3
|
|
|
|
| |
2. |
ni1
ta-ko-mo2
dzü(-no)3
ayi 4
kade pi-o5 |
|
|
see5
me4
before3
you(sg.)1
leave2
|
|
|
(iii)
|
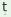 hi
‘after’ added to the participial form of the verb
denotes that the action of the main clause follows
the action of the subordinate clause. hi
‘after’ added to the participial form of the verb
denotes that the action of the main clause follows
the action of the subordinate clause.
|