| |
4.4.1. Perfective aspect :
|
| |
It
describes an action either completed in the past or to be
completed. In the present, it expresses the completion of
an action just finished. In future, it expresses the action
to be completed in near future. In the past, it expresses
the action done already. Aspect marker is -th kà
and it occurs in all the three tenses. kà
and it occurs in all the three tenses.
|
| |
4.4.1.1. Present perfect :
|
| |
It
expresses the completion of an action just finished, Present
perfect aspect marker is -th kà.
When the present perfect aspect marker is added to the verbs
present tense marker does not occur. Structure of the verb
in the present perfect is as follows : kà.
When the present perfect aspect marker is added to the verbs
present tense marker does not occur. Structure of the verb
in the present perfect is as follows :
|
|
Verb
stem + Aspect Marker
|
|
Examples
1.  -n -n
 ts ts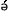 ts
ts -th -th kà kà
I-nom egg eat-perfect
I have eaten egg
2. mp -n -n kákò móts
kákò móts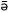  à
kh à
kh -th -th kà kà
He-nom book a read perfect
He has read a book
|
| |
4.4.1.2. Past Perfect : |
| |
This
aspect expresses the action done long ago. Past perfective
marker is also -th kà.
In the case of past perfect, past tense marker is not dropped
as it was done in the present perfect, the perfect marker
is added to the stem and the tense marker occurs in the
end. The structure of the past perfect aspect verb is as
follows : kà.
In the case of past perfect, past tense marker is not dropped
as it was done in the present perfect, the perfect marker
is added to the stem and the tense marker occurs in the
end. The structure of the past perfect aspect verb is as
follows :
|
|
Verb
Stem + Aspect Marker + Tense Marker |
|
Examples
1.  -n -n ótsì ts
ótsì ts -th -th k-chò k-chò
I-nom rice eat-perfect marker-past
I had eaten rice
2.
mp -n -n
 rá rá khí-th
khí-th k-chò k-chò
He-nom money take-perfect marker-past
He had taken money
|
| |
4.4.1.3. Future perfect :
|
| |
This
expresses the action to be completed in near future. Future
perfect aspect marker is also -th kà,
future tense marker is added to the past perfect aspect
form. Future tense marker is -v. Structure of the verb in
future perfect is as follows : kà,
future tense marker is added to the past perfect aspect
form. Future tense marker is -v. Structure of the verb in
future perfect is as follows :
|
|
Verb
Stem + Aspect marker + Past marker + Future marker |
|
Examples
1.  -n -n
 lh lh c
c tsh
tsh -th -th kà-chò-v kà-chò-v
I-nom work the do-perfect-past-future
I should have done that work
|
|
2.
 -n -n ótsì ts
ótsì ts -th -th kà-chò-v kà-chò-v
I-nom rice eat-aspect-past-future
I should have eaten rice
|
|
One
can notice from the examples of present, past and future
perfect aspects that when the verdb is used in the present
and future perfect aspects, the marker -th kà
is used in its full form, whereas in the case of past perfect
the final -à of aspect marker th kà
is used in its full form, whereas in the case of past perfect
the final -à of aspect marker th kà
is dropped and it becomes th kà
is dropped and it becomes th k
as can be seen in the above examples. k
as can be seen in the above examples.
|
| |
4.4.2. Imperfective or Durative aspect :
|
| |
It
describes an action which is regarded as continuous in
the past or present. Durative aspect marker is -v n n .
Structure of the verb in the durative aspect is as follows
: .
Structure of the verb in the durative aspect is as follows
:
|
|
Verb
Stem + Durative Marker + Tense Marker |
| |
4.4.2.1.
Past durative : |
| |
Examples
1. mp -n -n yé
yé -t -t n n
 pá-v pá-v n-chò n-chò
He-nom day all sleep-durative-past
He was sleeping all the day |