Inflection is a morphological process by which words are
formed with the help of bound forms which are
called inflectional affixes. Inflected words belong to the same
form-class to which the root word
belongs.
|
Derivation is a
morphological process which is concerned with the structure of
the stems. In other words, word stems are
formed by derivation. Two types of this process are generally
distinguished and they are compounding
and derivation. Compounding is a derivational process in
which a stemi s formed with two
roots, the resultant stem belonging to the form class of at
least one of the constituent roots.
|
| |
Derivation is a
process of word formation in which a stem is formed with two
roots or a root and an affix and the
resultant stem does not belong to the form class of any of the
constituents.
Both inflectional and
derivational affixes are involved in affixation.
Depending on their position of occurrence with respect
to the root, the affixes are classified into prefixes,
suffixes and infixes.
Prefixes precede the root; suffixes follow it, and infixes occur
within the root.
Reduplication is
another morphological process in which ia part of a root or the
root itself is added to the root.
|
|
|
Contraction is a process of word
formation in which a syllable is dropped from the root.
|
In Karbi words are
formed using different morphological process, viz., inflection,
compounding, derivation, affixation,
reduplication, and contraction. Both prefixes and suffixes occur
in Karbi. The prefixes are
used to form derived adjectives, verbal noun, agent noun,
causatives and reciprocal. The suffixes denote
gender, number, honorific, case, tense, aspect and modal.
Examples are given below to illustrate the
various processes in Karbi.
|
| Inflection: |
|
| dam |
‘go’ |
| damlo |
‘went’ |
| dampo |
‘will go’ |
va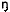 |
‘come’ |
va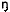 non non
|
‘come (Imp.)’ |
|
|
|
|
|