| 3.3.13.5 |
General
Remarks about Simple Adverbs |
|
All
these five categories of adverbs are known as simple
adverbs. These adverbs describe the manner, the time
and the locus of accomplishment of the actions suggested
by the verbs. Of these five categories the first one
is the dominant one and it has a large number of members. |
|
There
are a large number of adverbial expressions to describe
actions in relation to specific actors by means of which
appearance, nature, state, existence, characteristics
etc. of the actions or actors can be conveyed to the
hearer conveniently. It is interesting to note that
Hmar uses some adjectivals referring to ‘big’, ‘small’,
‘quite’, ‘noisy’ etc. in reduplication to, infact, modify
the action of the verb in a sentence. For example if
there is a word /u:l/ ‘big’ in reduplicated form after
a verb it will mean that the relevant subject noun does
something ‘loudly’, ‘with force’ etc. The following
examples given in pairs of sentences with broad. English
gloss could be seen. |
/á:r
à khúo ú:l ù:l/
ú:l ù:l/ |
‘cock crows big sound (=loudly)’
|
| /á:r
à khúoN á:l à:l/ |
‘cock crows small sound(=mildly)’
|
/vàté
à vúo dúoi dùoi/
dúoi dùoi/ |
‘bird flies big (=fast)’ |
/vàté
à vúo líei/díei/
líei/díei/ |
‘bird flies small(=slowly)’ |
/a
tlá:n vù vú
vú / /
|
‘he runs big (=much), and not go fast’
|
/a
tlá:n vù vá
vá /vè /vè vé
vé / /
|
‘he runs small (=little), quick and fast’
|
/a
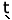 hú hú kú:k èl/
kú:k èl/ |
‘he sits big’ |
/a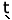 hú hú ká:k èl/
ká:k èl/ |
‘he sits small’ |
| /á:n
nám bùt/ |
‘it smells big (=strong)’ |
| /á:n
nám bàt/ |
‘it smells/small(=not so strong)’
|
| |
|
|
The
manner of production of any kind of sound or emanting
any kind of smell could be described in this way. This
can be done by the reduplicated
use of some non-lexical items converging the senses
as above. This is a peculiarity of Hmar |
|
| 3.3.13.8 |
Adverbs
Derived from Nouns |
|
A
few adverbs of manner are derived from nouns by suffixing
{-tin}. There does not seem to be any perceptible morphophonemic
change. The following examples could be seen: |
| Noun
|
Adverbs
|
| /kùm/ |
‘year’ |
/kùm-tìn/ |
‘yearly’ |
| /ní/ |
‘day’ |
/ní-tín/
|
‘daily’ |
| /sù:n/ |
‘day’ |
/sù:n-tìn/
|
‘daily’ |
| /thlà/ |
‘month’ |
/thlà-tìn/
|
‘monthly’ |
| /hàptá/ |
‘week’ |
/hàptá-tín/
|
‘weekly’ |
|
|
|
|
|
| 3.3.13.9 |
Adverbs
Derived from Advectives |
|
Ouite
a large number of adverbs of manner are derived from
adjectives by suffixing {-takin}. Here also no morphophonemic
changes take place. |
|
|