kò ã ã |
na |
kh m m |
hota |
d€
|
we |
U ta ta
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
| |
|
‘If
|
horses
|
had |
wings |
they |
would |
have |
flown’ |
|
1-2 |
4 |
3 |
6 |
|
|
7 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
If
|
you |
go (wish to go) |
then |
go |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
(ii)
|
/ji cIri cIr/ ‘until unless, till’ discontinuous co referential
connectives join the two clauses in which /ji cIr/
introduces the first clause and /i cIr/ begins the second clause. The
complex sentences so formed with these co referential connectives begin
with the conditional clause which also function as temporal adverbial of
the sentence. Examples are : |
| |
|
ji
|
cIr i
|
k m m |
ní |
k rto rto |
i |
cIr t |
chUţţi |
ní |
mIl |
|
| |
|
‘Until
|
and
|
unless
|
you
|
do
|
the
|
work
|
you
|
will
|
not
|
get |
leave’ |
|
| |
|
ji
|
cIr
|
tũ
|
aw€go
|
i
|
cIr
|
hũ
|
Itt€
|
r ũgo ũgo
|
|
| |
| ‘Till |
you |
come |
I |
shall |
stay |
here’ |
|
|
(iii)
|
jItno---Itno/Utno ‘as much--as/ jItno--occurs with the clause
which is subordinate and Itno/Utno with the main clause. The subordinate
clause functions as degree or quantitative adverbial to the sentence. As
far as the order of the clauses is concerned any of the clauses can
precede. Examples are: |
|
jItno
|
tũ
|
d€go
|
hũ
|
Utno
|
le
|
lyũgo
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
| |
|
‘As
|
much |
you |
give |
that |
much |
I |
will |
take’ |
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
|
5 |
4 |
|
6-7 |
|
| |
|
Us
|
n €
|
khinu
|
Itni
|
dur
|
ph kyo kyo
|
jItno |
wo |
ph k k |
s k€ k€
|
tho
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
|
|
|
|
He
|
threw |
the |
ball |
as |
far |
away |
as |
much |
he |
could |
|
1-2
|
6 |
|
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
|
7 |
8 |
9-10-11 |
|
|
(iv) /je-tã/
‘If-then’
|
|
/je/ begins the first clause which is a conditional one and /tã/
begins the second clause. The second clause takes the finite verb in
present, past, and future tense depending on the verbal form of the
preceding clause.
|
|
Examples are:
|
|
je
|
wo
|
Ut
|

|
tã
|
c g g o o
|
|
‘If
|
he
|
is
|
there
|
then
|
there
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
1 |
2 |
4 |
3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
wEÛgo
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
will
|
be
|
a
|
quarrel’
|
|
|
| 7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
6 |
|
|
|
| |
|
je
|
wo
|
k m m
|
k r€ r€
|

|
tã
|
b l l
|
r
|

|
|
‘If
|
he
|
works
|
then
|
he
|
remains
|
healthy’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
|
1 |
2 |
2-4-5 |
6 |
|
8-9 |
7 |
|
| |
|
je
|
wo
|
Ut
|
tho
|
tã
|
c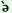 g g o o
|
‘If
|
he
|
was
|
there
|
so
|
there
|
|
1
|
2
|
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
1 |
2 |
4 |
3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
hoyo
|
|
|
|
|
|
was
|
a |
quarrel’ |
|
|
|
| 7 |
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
Complex sentences with Relative clauses
|
|
All these clauses are constituted of {j-} ‘who’ and occur as
subordinate clause in the complex sentences. Relative clauses occur as the
subject, object or the sentence complement of the complex sentence.
Relative
|