clause always
occurs as the part of the nominal phrase of the complex sentence and tells
the state of any of the nouns. In the language the relative clause has
three positions of occurrence (i) it can occur in the beginning of the
sentence; (ii) it can also occur after the main clause and (iii) it can
also occur after subject noun or object noun i.e. with in the main clause
of the complex sentence.
|
|
(1)
|
Relative clauses function as subject NP. In complex sentences the
subordinate clause occurs as the part of the subject. Examples are :
|
|
jé o o
|
Ut
|
kh  o o
|
tho
|
wo
|
mero
|
pài
|

|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
| |
|
‘The(one)
|
who
|
was
|
standing
|
there,
|
he
|
is
|
my
|
brother’ |
|
1 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
5 |
8 |
6 |
7 |
|
| |
|
jé o o
|
m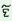
|
Us
|
na
|
kéyo
|
tho
|
wo |
s c c |
tho
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
|
| |
|
Whatever
|
I
|
said
|
to
|
him,
|
that
|
was
|
truth’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
3 |
7 |
9 |
8 |
|
| |
|
jIs
|
j  a a
|
n€
|
y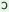
|
k m m
|
kIyo
|
wo
|
mero
|
pài
|

|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
9 |
9 |
10 |
|
| |
|
The
|
man |
who |
has |
done |
this |
work |
is |
my |
brother |
|
2-3 |
1 |
|
6 |
4 |
5 |
10 |
8 |
9 |
|
| |
|
ye
|
j  a a
|
ku
|
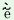
|
jé a a
|
hU
|
aya
|

|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
| |
|
Who
|
are |
these |
persons |
who |
have |
come |
now |
| 3 |
4 |
1 |
2 |
5 |
8 |
7 |
6 |
|
|
(2)
|
Relative clause occurring as object NP in the complex sentences and thus
the subordinate clause functions as the sentence complement. As in the
above examples the clause was functioning as the modifier of the subject of
the main clause as well as the complex sentence, here the relative clause
is functioning as modifier of the object in the sentence.
|
|
m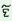
|
wo
|
dand
|
x ridyo ridyo
|
jé o o
|
|
‘I
|
bought
|
that
|
bullock
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
1 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
|
| |
|
c ngo ngo
|
tho
|
which
|
was
|
good’
|
|
6
|
7 |
5 |
7 |
6 |
|
| |
|
m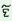
|
ek
|
gero
|
kuţyo
|
jo
|
ní
|
|
‘I
|
beat
|
one
|
boy
|
who
|
was
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
1 |
4 |
2 |
5 |
3 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
khy€
|
tho
|
|
|
|
|
|
not
|
eating’
|
|
|
|
|
|
7
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
gera
|
n€
|
wa
|
geri
|
s ddi ddi
|
|
‘The
|
boy
|
called
|
that
|
girl
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
|
1-2 |
5 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
jé i i
|
s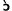  i i
|
thi
|
|
|
|
who
|
was
|
beautiful’
|
|
|
| 6 |
7 |
8 |
|
|
|
6 |
8 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
(3)
|
Relative clause also functions as adverbial but it would remain
the modifier of subject or object NP in the element /j-/ occurs as the
modifier of the noun or noun phrase but functions as the temporal,
location, manner etc. adverbial depending on the noun with which it
occurs. Examples:
|
|
jIs
|
we 
|
m
|
wo
|
dekhyo
|
wo
|
bUn
|
l mmo mmo
|
p yo yo |
wo |
tho
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
|
| |
|
‘When (the moment)
|
I
|
saw
|
him,
|
he
|
was
|
lying
|
down
|
straight’ |
|
1-2
|
3 |
5 |
4 |
6 |
11 |
9-10 |
7 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|