Besides some
of the adverbs such as proximate, remote adverbs of place and direction
can also occur together to form the compound adverbs. For example :
|
|
It-Ut
|
‘here and there’
|
|
Ingã-Ungã
|
‘this side that side’
|
|
|
There is another compound adverb formed by adding /Ik/ the alternant of
/ek/ ‘one’ to the adverb of time.
|
For example :
|
|
ch ţ-Ik ţ-Ik
|
‘for a while’
|
|
k d-Ik d-Ik
|
‘sometimes’
|
|
|
There is one expression for ‘this year’ which is a compound form
from the contraction of the alternant form of demonstrative pronoun and
the alternant of ‘year’ and this form is /Esũ/
‘this year’ as in :
|
|
Esũ
|
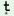 h h n n
|

|
‘It
|
is
|
cold
|
this
|
year’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
|
3 |
2 |
|
1 |
|
|
We find the corresponding temporal modifiers which are used in adverbal
phrase of time with /sal/ ‘year’ as in.
|
|
p r
sal r
sal
|
|
‘last year’
|
|
 gl€
sal gl€
sal
|
|
‘next year’
|
|
etc.
|
|
|
|
Some forms function both as
adjectives and adverbs :
|
|
There are some forms which are used as adjectives and are also used as
adverbs modifying the verbs. In the noun phrases these occur as modifiers
of the nouns and are in agreement with the gender-number of the head noun.
And as adverbs (if inflected) these agree with the gender-number of the
verb but in case of the verbs inflected for person-number these adverbs
agree with the gender-number of the subject. For example :
|
|
/k has--/
|
|
|
|
|
‘too
|
much’
|
as
|
adjective
|
in :
|
|
Us
|
n€
|
khaso
|
k m m
|
kIyo
|
‘He
|
did
|
plenty
|
of
|
work’
|
|
1
|
2
|
3 |
4 |
5 |
1-2 |
5 |
3 |
|
4 |
|
| |
|
khasa
|
j  a a
|
It
|
aya
|
‘Many
|
people
|
came
|
here’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
2 |
4 |
3 |
|
|
(In the above sentences /khaso
k m/
and /khasa
j m/
and /khasa
j 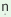 a/
are noun phrases occurring as object and subject respectively. /khaso/
is masculine singular because of its gender-number agreement with /k a/
are noun phrases occurring as object and subject respectively. /khaso/
is masculine singular because of its gender-number agreement with /k m/
and khasa/
is masculine plural as to agree with /j m/
and khasa/
is masculine plural as to agree with /j 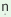 a/
which is masculine plural noun. a/
which is masculine plural noun.
|
|
/khas-/
functioning as adverb:
|
|
| |
|
m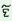
|
wo
|
khaso
|
maryo
|
‘I
|
beat
|
him
|
too
|
much’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
2 |
|
3 |
|
| |
|
m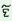
|
we
|
khasa
|
marya
|
‘I
|
beat
|
them
|
too
|
much’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
2 |
|
3 |
|
Some other forms functioning as adverbs like in the above example.
|
|
gero
|
cIrko
|
ayo
|
‘The
|
boy
|
came
|
late’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
|
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
geri
|
cIrki
|
ai
|
‘The
|
girl
|
came
|
late’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
|
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
wa
|
taw i i
|
ai
|
‘She
|
came
|
soon’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
tũ
|
b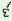 lo lo
|
ja
|
‘You
|
go
|
soon’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
s p p
|
 Ing-p Ing-p  Ingo Ingo
|
|
‘The
|
snake
|
moves
|
zig-zag’
|
|
1
|
2 |
|
|
1 |
3-4 |
2 |
|
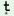 ur€ ur€
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Like adjectives present participial forms also function as adverbial
and in that case these occur preceding the verb and also shows the
agreement. Examples:added for the
formation of various adverbs listed in the above table.
|