|
Derivation of ther adverbs :
|
|
There are few suffixes which are very productive in the formation of
adverbs and these suffixes are added to noun, adjective and adverb storms.
These suffixes are /-ũ/,
/-€/
and /-ã/
/-ũ/
always marks notational ablative; /€/
marks location of place and time and /ã/
denotes directional as well as order adverbs. /-ũ/
is only added to the nouns and adverbs ending in consonants and /-€/
can be added to any stem and when this suffix is added then the gender
number marker is dropped. (see Case also). Examples are :
|
|
Adverbs with /-ũ-/
suffix
|
|
Uprũ
|
‘from up’
|
Uttũ
|
‘from there’
|
|
Ittũ
|
‘from here’
|
kIttũ |
‘from where’
|
|
 ndrũ ndrũ
|
‘from inside’
|
sIrũ |
‘from head
|
|
|
|
completely,
|
|
|
|
totally’ |
|
|
Adverbs with /-€/
suffix
|
|
pIchI€
|
‘last’
|
sIr€
|
‘corner’
|
|
jyad€
|
‘more’
|
bU € €
|
‘down’
|
|
t  € €
|
‘day’
|
pas€
|
‘towards’
|
|
kId€
|
‘somewhere’ |
 j€ j€ |
‘still’
|
|
s be be € €
|
‘in the morn- |
 gg€ gg€ |
‘ahead’
|
|
ing; |
|
|
|
pIcch€
|
‘behind’
|
parl€ |
‘that side,
|
|
|
|
other side’
|
 rarl€ rarl€ |
‘this side’ |
|
|
|
|
Adverbs with /-ã/
suffix
|
| |
|
p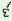 lã lã
|
‘before’
|
Ufrã
|
‘towards up’
|
|
 jã jã
|
‘still’
|
|
|
|
|
A few examples showing their use in sentences
|
|
wo
|
kyũ
|
geyo
|
‘Why
|
did
|
he
|
go’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
|
| |
|
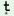 ndrũ ndrũ
|
tũ
|
kyũ
|
ayo
|
‘Why
|
did
|
you
|
come
|
from
|
inside’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
3 |
4 |
2 |
4 |
|
1 |
|
| |
|
wo
|
kIttũ
|
ayo |

|
‘Where
|
has
|
he
|
come
|
from’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
2 |
4 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
Us
|
n€
|
p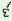 lã lã
|
wi |
y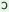
|
‘He
|
has
|
done
|
this
|
work
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
1-2 |
8 |
7 |
5 |
6 |
|
k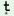 m m
|
kIyo |

|
|
|
before
|
also’
|
|
|
|
6
|
7 |
8 |
|
|
3 |
4 |
|
|
|
| |
|
wo
|
 gg€ gg€
|
b€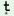 ho ho
|

|
|
‘He
|
is
|
sitting
|
in
|
the
|
front’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
4 |
3 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
etc.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compound Adverbs :
|
|
There are some compound adverbs in which two stems occur and these
denote various adverbial functions. Many of the compounds are formed by
repeating the adverbial form with or without some linking affix and all
such adverbs denote frequency. Linking affix /-o-/ occurs when the adverb
repeated one is consonantal ending. Examples are :
|
|
ph 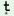 -o-ph -o-ph ţ ţ
|
‘quickly’
|
|
k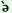  i-k i-k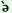  i i
|
‘again and again’
|
|
b l l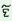 -b -b l l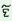
|
‘slowly’
|
|
k de-k de-k de de
|
‘sometimes’
|
|