And perfective
participle denotes simple past.
|
|
Us
|
n€
|
kà
|
k pyo pyo
|
‘He
|
cut
|
the
|
grass’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
1-2 |
4 |
|
3 |
|
|
(iii) Future :
|
|
It indicates that the event will occur. Future has two stem forming
suffixes {-g-} occurring after the contingent form that takes the
gender-number suffixes and {-s-} occurs after other stems like
intransitive, transitive, causal and person-number suffixes are added to
it.
|
|
gero
|
p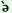   k k
|
jy€go
|
‘The
|
boy
|
will go
|
tomorrow’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
|
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
geri
|
p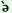   k k
|
jy€gi
|
‘The
|
girl
|
will go
|
tomorrow’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
|
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
gero
|
p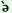   k k
|
n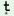 í í
|
jas€
|
‘The
|
boy
|
will
|
not
|
go
|
tomorrow’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
|
|
3 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
geri
|
p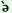   k k
|
ní
|
jas€
|
‘The
|
girl
|
will
|
not
|
go
|
tomorrow’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
4 |
3 |
4 |
2 |
|
|
Besides the imperative also refers to futurity.
|
E.g.
| tũ
|
mInna |
ek |
gã
|
d Iye Iye
|
‘(Please)
|
give
|
me
|
a
|
cow’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
5 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
t m m
|
mInna |
ek |
gã
|
d Iyo Iyo
|
‘(Please)
|
give
|
me
|
a
|
cow’ |
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5
|
|
5 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
5 Aspect :
|
|
Aspect indicates the nature of the time of action of a verb as to its
beginning, duration, completion or repetition. According to Comrie*-’Aspects
are different ways of viewing the internal temporal constituency of a
situation’. The inflected verbal forms like imperfective, perfective,
contingent with present auxiliary etc. denote aspects. A few examples show
the contrast of aspects:
|
|
(i) Imperfective :
|
|
This indicates the event in the process of completion. This aspect is
marked by the contingent form followed by the present tense auxiliary and
imperfective participle. Examples are.
|
|
|
|
wo
|
jy€
|
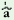
|
‘He
|
goes’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
1 |
2-3 |
|
| |
|
gera
|
jy
|
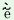
|
‘The
|
boys
|
go’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
|
1 |
2-3 |
|
|
|
|
wo
|
ní
|
jato
|
‘He
|
does
|
not
|
go’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
|
2 |
3 |
|
|
(ii) Perfective :
|
|
This indicates the completion of the event or action. This aspect is
always marked by the perfective participle forms of the verb. Examples
are.
|
|
wo
|
geyo
|
‘He
|
went’
|
|
1
|
2 |
1 |
2 |
|
| |
|
geri
|
n€
|
k m m
|
kIyo
|
‘The
|
girl
|
did
|
the
|
work’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1-2 |
4 |
|
3 |
|
| |
|
m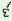
|
y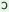
|
buţo
|
layo
|
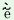
|
‘I
|
have
|
planted
|
this
|
tree/plant’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
* Comrie, Bernard 1976. ‘Aspect’, Cambridge University Press.
|