All the verbal forms have the
distinctions of number category but the number markers cannot be isolated in the language. Number markers are fused either with person
or with the gender. A few examples are:
|
|
hũ
|
jaũ
|
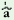 (Ip.sg.)
(Ip.sg.)
|
‘I
|
go’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
2-3 |
|
| |
|
h m m
|
jã
|
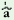 (Ip.pl.)
(Ip.pl.)
|
‘We
|
go’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
2-3 |
|
| |
|
wo
|
jyє
|
 (IIIp.sg.)
(IIIp.sg.)
|
‘He
|
goes’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
2-3 |
|
| |
|
we
|
jy
|
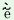 (IIIp.pl.)
(IIIp.pl.)
|
‘They
|
go’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
2-3 |
|
| |
|
gero
|
geyo |
tho
(mas.sg.)
|
‘The
|
boy
|
had
|
gone’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
|
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
gera
|
geya
|
tha
(mas.pl.)
|
‘The
|
boys
|
had
|
gonel’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
|
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
geri
|
g i i
|
thi
(fem.sg.)
|
‘The
|
girl
|
had
|
gone’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
|
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
| gerĩ |
g ĩ ĩ |
thĩ(fem.
pl.)
|
The
|
girls
|
had
|
gone’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
|
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
|
3 Person :
|
|
The distinction of the three persons of personal pronouns like the
person speaking, the person spoken to, and the person spoken about are
first, second and third person respectively are maintained in some verbal
forms by the suffixes termed person-number concording suffixes. The person
markers cannot be isolated in the language, these are fused with the
number markers. The person-number distinctions are found in present tense
auxiliary, future, contingent, imperative forms.
See 3.3.2. a and 3.3.3)
|
|
4. Tense
|
|
Each verbal form shows some time reference. There are three main tenses
present, past and future indicated by the various forms. Contingent,
imperfective participle denote mainly present tense whereas perfective
denote simple past and future tense is denoted by the future forms.
Besides / /
etc. /th-/ auxiliaries mark present and past tense respectively. A few
examples are : /
etc. /th-/ auxiliaries mark present and past tense respectively. A few
examples are :
|
|
(i) Present Tense
|
|
Contingent with auxiliary
|
|
|
|
wo
|
k m m
|
k r€ r€
|
 |
‘He
|
works’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
2-3-4 |
|
|
Imperfiective
|
| |
|
we
|
It
|
awẽ
|
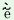 (IIIp.pl.)
(IIIp.pl.)
|
‘They
|
come
|
here’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
3-4 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
hũ
|
 j j
|
ní
|
ato
|
‘I
|
don’t
|
come
|
today’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
3 |
4 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
wo
|
k m m
|
ní
|
k rto rto
|
‘He
|
does
|
not
|
work’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
|
3 |
2-4 |
|
|
(ii) Past tense
|
|
Past tense is denoted by the past tense auxiliary.
|
|
|
|
wo
|
c ngo ngo
|
j  o o
|
tho
|
‘He
|
was
|
a
|
good
|
man’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
|
2 |
3 |
|
|
Perfective with past tense auxiliary deonotes remote past
|
| |
|
wo
|
geyo
|
tho
|
‘He
|
had
|
gone’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
|