|
|
(3) Future :
|
|
There are two future marking alternant {-g-~-s-}. From the above table
/cãkũgo/
etc. shows the agreement of person-number as well as gender-number because
{-g-} is added to the contingent form. The other alternant {-s-} is added
to the verbal stems directly and then take (a-1) person-number suffixes.
Thus this form shows the agreement of person-number suffixes. Thus this
form shows the agreement of person-number with the subject. Both these
future alternant forms are syntactically related as the latter form
exclusively occurs in the negative sentences. Examples are :
|
|
hũ
|
y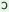
|
k m m
|
k rũgo rũgo
|
‘I
|
shall
|
do
|
this
|
work’
|
(Ip.sg.)
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
|
2 |
3 |
|
|
| |
|
hũ
|
hũ
|
y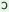
|
k m m
|
ní
|
k rsũ rsũ
|
‘I
|
shall
|
not
|
do
|
this
|
work’
|
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
1 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
2 |
3 |
(Ip.sg.) |
|
| |
|
wo
|
kà
|
k pp€go pp€go
|
‘He
|
will
|
cut
|
the
|
grass’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
1 |
|
3 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(IIIp.sg.)
|
|
| |
|
wa
|
kà
|
kpp€gi
|
‘She
|
will
|
cut
|
the
|
grass’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
|
3 |
|
2 (IIIp.sg)
|
|
| |
|
wo
|
kà
|
ní
|
k ps€ ps€
|
‘He
|
will
|
not
|
cut
|
the
|
grass’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
3 |
4 |
|
2 |
|
| |
|
wo
|
kà
|
ní
|
k ps€ ps€
|
‘She
|
will
|
not
|
cut
|
the
|
grass’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
3 |
4 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(IIIp.sg.) |
|
|
(4) Perfective Praticiple :
|
|
The perfective participial stem is formed by adding {-y- ~
f} to the verbal stem and then it takes the
gender-number suffixes. The verbal form shows the agreement of
gender-number with the subject of intransitive verb and with the direct
object (in the direct form) of the transitive verbs.
|
Examples :
|
|
(i) Transitive-object agreement
|
|
m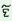
|
wa
|
 I I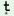 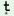 hi hi
|
‘I
|
saw
|
her’ (fem.sg.)
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
m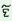
|
y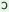
|
k m m
|
kIyo
|
‘I
|
did
|
this
|
work’ (mas. sg.)
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
|
| |
|
gera
|
n€
|
geri
|
kUţţi
|
‘The
|
boy(ag.)
|
beat
|
the
|
girl’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
2 |
4 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(fem.sg.)
|
|
| |
|
geri
|
n€
|
mewa
|
a ya ya |
‘The
|
girl(ag.)
|
brought
|
fruits’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
1-2 |
4 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mas.pl.)
|
|
|
(ii) Intransitive-subject agreement
|
|
gero
|
geyo |
‘The |
boy |
went’ |
(mas.sg.) |
| 1 |
2 |
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
| |
|
geri
|
cãki
|
‘The
|
girl
|
shouted’ (fem.sg.)
|
| 1 |
2 |
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
gera
|
do ya ya
|
‘The
|
boys
|
ran’ (mas.pl.)
|
| 1 |
2 |
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
gerĩ
|
do ĩ ĩ
|
‘The
|
girls
|
ran’ (fem.pl.)
|
|
1
|
2 |
|
1 |
2 |
|
| |
|
ger
|
n 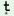 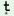 hĩ hĩ
|
‘The
|
girls
|
ran
|
away’(fem.pl.)
|
|
1
|
2 |
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
(5) Imperfective participle :
|
|
Like perfective participles, imperfective participial stem formed by adding
{-t-} takes gender-number
|