Explanation:
|
|
From the above inflectional suffixes and the conjugation tables we get
the following verbal forms:
|
(1) Contingent :
|
|
Contingent form is formed by adding (a-1) inflectional suffixes marking
person-number concordance to a verbal stem (intransitive, transitive,
causative and compound etc.). In this language this form marks
uncertainty etc. and always occurs in the indicative mood i.e. never
occurs in negative sentences. A few examples are :
|
|
hũ
|
jaũ
|
‘I
|
may go’
|
(Ip.sg.)
|
| 1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
wo
|
jy€
|
‘He
|
may go’
|
(IIIp. sg.)
|
|
1
|
2 |
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
tũ
|
bu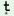 o o
|
k mpp€ mpp€
|
‘You
|
may cut the
|
tree’
|
(IIp.sg.)
|
|
1
|
2
|
3 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
|
|
(2) Imperative :
|
|
There are two types of imperatives marked by suffixes (a.2) and (a.3).
a. 2 marks immediate action whereas (a.3) marks the remote action. Besides
(a.2) is ordinary imperative marking order and (a.3) denotes the
politeness or request. Any verbal stem unmarked can occur as ordinary
imperative in IInd person singular except that the final geminated
consonants get simplified and verbal stem takes {-o} suffix for IInd
person plural. Besides, there are some monosyllabic stems ending in /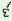 /
also takes {-o} suffix to denote IInd person singular imperative. Example
are : /
also takes {-o} suffix to denote IInd person singular imperative. Example
are :
|
|
Ordinary and Immediate Imperative
|
|
|
tũ
|
y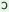
|
seu
|
k p p
|
‘You(sg.)
|
pluck
|
this
|
apple’(IIp.sg.)
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
t
|
ye
|
seu
|
k ppo ppo
|
‘You (pl.)
|
pluck
|
these
|
apples’
|
(IIp.pl.) |
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
| |
|
tũ
|
y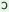
|
k m m
|
k r r
|
‘You (sg.)
|
do
|
this
|
work’
|
(IIp.sg.)
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
t m m
|
y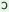
|
k m m
|
k ro ro
|
‘You(pl.)
|
do
|
this
|
work’ (IIp.pl.)
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
tũ
|
It
|
ró
|
‘You (sg.)
|
live
|
here’ (IIp.sg.)
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
tũ
|
ya
|
g l l
|
kó
|
‘You (sg.)
|
say
|
this
|
thing’ (IIp.sg.)
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
| tũ |
It
|
ló
|
‘You (sg.)
|
say
|
this
|
thing’ (IIp.sg.)
|
(IIp.sg.)
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
t m m
|
It
|
ró
|
‘You (pl.)
|
live
|
here’
|
(IIp.pl.)
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
|
|
(From the above examples /ró/
denotes both second person singular and plural imperative forms)
|
|
Polite and Remote Imperative :
|
|
tũ
|
y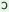
|
seu
|
k pIye pIye
|
‘Please
|
cut/pluck
|
this
|
apple’
|
(IIp.sg.)
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
t m m
|
ye
|
seu
|
k pIyo pIyo
|
|
‘You (pl.)
|
please
|
cut/ pluck
|
these
|
apples |
(IIp.pl.) |
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
4 |
|
2
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
tũ
|
y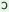
|
k m m
|
k rIye rIye
|
‘You (sg.)
|
please
|
do
|
this
|
work’
|
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4 |
1 |
4 |
|
2 |
3 |
|