suffixes which
always agrees with the nominal subject. In marks the imperfect in present
or past time. In this language when it occurs in the negative sentence it
always marks present imperfect. A few examples are :
|
|
je
|
wo
|
ato
|
‘If
|
he
|
would
|
have
|
come.’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
(mas.sg.) |
|
| |
|
wo
|
p  to to
|
d€
|
pas
|
ho
|
jato
|
‘If
|
he
|
studied
|
he
|
would
|
have
|
passed.’ |
|
1
|
2
|
3 |
4 |
5 |
6
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
4-5-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mas.sg.) |
|
| |
|
geri
|
k m m
|
nÍ
|
k rti rti
|
‘The
|
girl
|
does
|
not
|
work’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
|
3 |
2-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(fem.sg.) |
|
| |
|
gerĩ
|
bu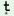 a a
|
ní
|
k pti pti
|
‘The
|
girls
|
do
|
not
|
cut
|
the
|
trees’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
|
3 |
4 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(fem.pl.) |
|
|
(6) Infinitive :
|
|
Infinitive stem is formed with {-¸-}
suffix added to any verbal stem (primary or causal etc.) and to this
infinitive stem gender-number suffixes are added to get this form. With
this form subject occurs with the post-position {-n€-}
or {na} or ergative pronouns. The transitive form of the verb always shows
agreement like perfective participle form with the object and intransitive
verb always occurs with masculine singular inflection. The form always is
followed by the tense auxiliary in the declarative sentences.
|
|
A few examples are :
|
|
(Transitive-Object agreement)
|
|
|
m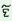
|
 ogi ogi
|
ma
|
pa i i
|
la o o
|

|
‘I
|
have
|
to
|
water
|
the
|
field’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
1 |
6 |
|
4-5 |
|
2-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mas.sg.) |
|
|
|
|
Us
|
n €
|
ló
|
pher i i
|

|
‘He
|
has
|
to
|
iron/press’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
1-2 |
5 |
|
3-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(fem.sg.) |
|
|
(Intransitive-non agreement)
|
|
|
mInna
|
ja o o
|

|
‘I
|
have
|
to
|
go’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
m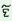
|
ja o o
|
 |
‘I
|
have
|
to
|
go’
|
|
1
|
2
|
3 |
1 |
3 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
Unnã
|
nє
|
a o o
|
tho
|
‘They
|
had
|
to
|
come’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
1-2 |
4 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mas. sg.)
|
|
(Transitive-Object non-agreement)
|
|
|
m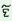
|
Us
|
na
|
daw t t
|
w r r
|
s d d o o
|

|
‘I
|
have
|
to
|
invite
|
him
|
for
|
feast’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
|
1 |
7 |
|
6 |
4-3 |
5 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mas.sg.)
|
|
|
|
|
m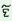
|
geri
|
na
|
mar o o
|

|
‘I
|
have
|
to
|
beat
|
the
|
girl’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
|
4 |
|
2-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mas.sg.)
|
|
|
Non-finite use:
|
|
Obliqe form of the infinitive occurs like a noun
|
|
hũ
|
It
|
a
|
na
|
caũ
|
‘I
|
want
|
to
|
come
|
here’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
|
3-4 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
hũ
|
m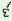 s s
|
na
|
h r r
|
t  € €
|
car 
|
wast€ |
le |
jau |
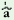
|
‘I
|
take
|
the
|
buffalo
|
every
|
day
|
for
|
grazing’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6
|
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
1 |
8-9-10 |
|
2-3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
hũ
|
pa i i
|
ma
|
t r r 
|
na
|
p sInd sInd
|
k rũ rũ |
‘I
|
like
|
to
|
swim
|
in
|
the
|
water’
|
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
1
|
6-7
|
5 |
4 |
3
|
|
2 |
|