So {-I-} in
(3) is the polite marker followed by the person-number marker.
|
|
(b) Gender-Number suffixes
|
|
Singular
|
Plural |
|
Masculine
|
-o |
-a |
|
Feminine
|
-i
|
-ĩ
|
|
|
(c) Following are the stem formative suffixes to which the above
person-number or gender-number suffixes are added. These suffixes mark
various tense and aspect.
|
|
(i)
|
{-s-~-g-} |
future marking stem formatives |
|
|
/-s-/ takes the above (a-1)
|
|
|
suffixes marking person-
|
|
|
number and added to the
|
|
|
verbal stems. |
|
|
|
|
|
/-g-/ takes the gender-number
|
|
|
suffixes and added to the stems
|
|
|
after taking (a-1) suffixes.
|
|
|
|
(ii)
|
{-y-~-f-}
|
perfective participle suffix
|
|
|
which
takes gender-number suffix. /-f-/
is added to the consonantal ending alternant of some other stem like
/l bb-/
‘find’ /l bb-/
‘find’ /l g-/
‘fix’. /-y-/ is a added to other stems. g-/
‘fix’. /-y-/ is a added to other stems.
|
|
|
|
|
(iii)
|
{-t-} |
imperfective participle and it takes gender-number suffixes. |
|
(iv)
|
{- 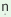 -~n-} -~n-}
|
infinitive stem formative and takes gender-number suffixes
/-n-/ infinitive stem formative occurs after the stems ending is non-stop retroflex and all
the other take /-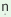 -/. -/.
|
|
|
The paradigms of /cãk/
‘shout’ with all the suffixes are listed here for illustration.
|
|
|
Singular
|
Plural |
|
Contingent:
|
Ist
|
cãkũ
|
cãkã
|
|
IInd
|
cãk€
|
cãkẽ
|
|
IIIrd |
cãk€ |
cãkẽ |
|
Future:
|
Ist
|
cãksũ
|
cãksẽ
|
|
IInd
|
cãks€
|
cãksẽ
|
|
IIIrd
|
cãks€
|
cãksẽ
|
|
Ordinary Imperative:
|
IInd
|
cãk |
cãko
|
|
Polite Imperative:
|
IInd |
cãkIyo
|
cakIyo
|
|
Perfective:
|
Mas. |
cãkyo |
cãkyo
|
|
Fem.
|
cãki |
cãkĩ
|
|
Imperfective:
|
Mas. |
cãkto |
cãkta
|
|
Fem.
|
cãkti |
cãktĩ |
|
Infinitive:
|
Mas. |
cãk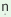 o o |
cãk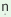 a a
|
|
Fem.
|
cãk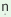 i i |
cak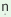 ĩ ĩ
|
|
|
Singular
|
|
|
Plural |
|
|
| Future: |
Ist |
IInd |
IIIrd |
Ist |
IInd |
IIIrd |
|
Mas.
|
cãkũgo
|
cãk€go
|
cak€go
|
cãkãga
|
cãk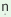 ga ga
|
cãk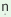 ga ga
|
|
Fem.
|
cãkũgi
|
cãk€gi
|
cãk€gi
|
cãkãgĩ
|
cãk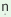 gĩ gĩ
|
cãk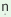 gĩ gĩ
|
|