| wo
|
mera |
dũ |
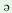 g€ g€
|
b€ ho ho
|
wo |
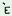
|
|
‘He
|
is
|
sitting
|
in
|
front
|
of
|
me’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5
|
6 |
7 |
|
1 |
7 |
5-6 |
|
4 |
|
2-3 |
|
| |
|
wo
|
mera
|
dũ
|
p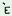 lã lã
|
tho
|
|
‘He
|
was
|
ahead
|
of
|
me’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
1 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
|
|
(ii) Temporal Locative :
|
|
It marks the action performed in relation to location of time. This is
marked almost by the same forms as place or directional locative except
these forms follow the nouns marking the time. A few examples are :
|
|
wo
|
d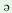 s s
|
b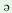 ja ja
|
dũ
|
pIcch€
|
ayo
|
|
‘He
|
came
|
after
|
ten
|
O’clock’
|
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
1 |
6 |
4-5 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
wo
|
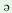 ndera ndera
|
dũ
|
p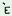 lã lã
|
geyo
|
|
‘He
|
went
|
before
|
the
|
dark’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
1 |
5 |
4 |
|
2-3 |
|
|
|
|
wo
|
p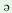 nj nj
|
b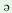 ja ja
|
to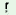 i i
|
k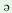 m m
|
m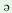 ka ka
|
d€go
|
|
‘He
|
will
|
finish
|
the
|
work
|
by
|
5
|
O’clock’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
1 |
|
6-7 |
|
5 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
(iii) Directional Locative :
|
|
Direction locative is marked by three postpositions {d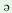 r},
{to r},
{to i}
and {t i}
and {t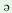 k}.
Besides {to k}.
Besides {to i}
and {t i}
and {t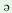 k}
have destination meaning also. Examples are : k}
have destination meaning also. Examples are :
|
|
Us
|
d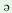 r r
|
dekh
|
|
‘Look
|
at/towards
|
him’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
|
3 |
2 |
1 |
|
| |
|
wo
|
tera
|
to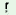 i i
|
ayo
|
|
‘He
|
came
|
upto
|
you’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
gero
|
ap a
|
k r r
|
to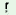 i i
|
geyo
|
|
‘The
|
boy
|
went
|
upto
|
his
|
home’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
|
1 |
5 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
|
| |
|
And
|
also
|
{t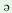 k} k}
|
occurs
|
freely
|
with
|
{to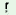 i}. i}.
|
|
| |
|
wo
|
k r r
|
t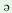 k k
|
geyo
|
|
‘He
|
went
|
upto
|
home’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
Adjectives are defined syntactically as class of words which occur as
modifier of nouns in noun phrases and also as complement of noun in the
copula sentence. For example :
|
|
nIkko
|
k r r
|
|
‘small
|
house’
|
|
1
|
2 |
|
1 |
2 |
|
| |
|
c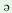 ngo ngo
|
gero
|
|
‘good
|
boy’
|
|
1
|
2 |
|
1 |
2 |
|
| |
|
karigi
|
geri
|
|
‘wise
|
girl’
|
|
1
|
2 |
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
And also in copula sentences :
|
|
y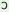
|
k r r
|
nIkko
|
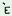
|
|
‘This
|
house
|
is
|
small’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
2 |
4 |
3 |
|
| |
|
y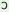
|
gero
|
c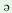 ngo ngo
|
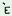
|
|
‘This
|
boy
|
is
|
good’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
2 |
4 |
3 |
|
| |
|
ya
|
geri
|
c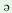 ngi ngi
|
|
|
‘This
|
girl
|
is
|
good’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
2 |
4 |
3 |
|
|
In all the above constructions /nIkko/,/c ngo/,/karigo/
adjectives are denoting the quality of the nouns with which they are
occuring as modifiers. ngo/,/karigo/
adjectives are denoting the quality of the nouns with which they are
occuring as modifiers.
|