Examples :
|
| jhu:lla |
‘swing’ |
jh r: r: n n |
‘brook’ |
jh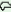 lm lm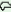 l l |
‘to
shine’ |
| jho:rka |
‘window’ |
| jhlmki |
‘twin’ |
b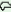 jh^w jh^w |
‘to
understand’ |
|
|
[s], alveolar voiceless fricative, is produced as this: the blade
of the tongue is raised towards alveolar region to form a narrow
opening between the blade of the tongue and alveolar region. The
tongue is contracted sideways and a groove is formed along the
middle of the tongue. The air from the lung passes through the
narrow opening causing friction. The vocal cords do not vibrate.
|
|
Examples:
|
|
sa:n |
‘fuel’ |
|
s^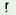 a a |
‘word’ |
|
sI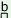 Il Il |
‘taste’ |
|
s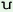 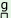 ^ ^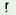 u u |
‘beautiful’ |
|
s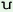 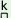 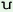 ri ri |
‘pig’ |
|
p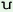 s^k s^k |
‘dress’ |
|
t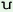 sIn sIn |
‘to
put on (shoes)’ |
|
m^sk^l |
‘lamp’ |
|
bEsn^m |
‘to
love’ |
|
ra: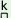 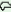 s s |
‘demon’ |
|
s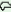 ndEs ndEs |
‘doubt’ |
|
|
[m], bilabial voiced nasal consonant, is produced as this: the
oral passage is blocked completely by closing the lips. The soft
palate is lowered so that the air passes through nasal passage.
The vocal cords are vibrating.
|
Examples :
|
m^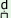 i i
|
‘cooked rice’ |
| m^ja
|
‘fibre’ |
| m^r^ŋ |
‘big’ |
m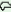 ča ča |
‘mouth’ |
dh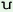 m^ŋ m^ŋ
|
‘drum (made of wood)’ |
| rImbIl |
‘cloud’ |
k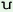 mba mba
|
‘hut’ |
s^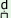  m m
|
‘horse’ |
hlr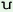 m m
|
‘co-wife’ |
|
[ n ], dental voiced nasal consonant, is
produced as this: the oral passage is blocked completely by raising the
tongue tip against teeth ridge. The soft palate is lowered and the arrested
air pases through the nasal passage. The vocal cords are vibrating.
|
Examples :
|
| l^nda
|
‘to laugh’ |
g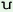 nda nda
|
‘to pulverize’ |
s nd nd r r
|
‘pus’ |
| bIndh^¸i
|
‘to betroth’ |
č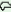 ndIri ndIri
|
‘limestone’ |
| mEnd^?
|
‘tears’ |
h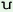 nd nd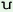 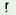 i i
|
‘shed (cock or hen)’ |
|
[n], alveolar voiced nasalconsonant, is
produced as this: the oral passage is blocked by raising the tip of the
tongue against alveolar region. The soft palate is lowered and the arrested
air passes through the nasal passage. The vocal cords are vibrating.
|
Examples :
|
| nu |
‘to drink’ |
no: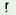 i i |
‘tube’ |
|