|
|
| ‘Soma does not buy fruits’ |
|
2. For the negation of existence, bano is used
as seen in the following sentences.
|
7. |
aiŋ-a |
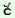 hori hori
|
bano-jan - a |
| |
I-case |
knife |
neg - tense - cop |
|
| ‘There was no knife with me’ |
|
8. |
ga·a-re |
da?a |
bano-jan - a |
| |
river-case |
water |
neg-tense-cop |
|
| ‘There was no water in the river’ |
|
3. -ge is emphatic marker in the language. It
is added with the negative marker ka-to negate the identity as seen in the following sentences :
|
9. |
kage, |
¸ia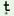 a a |
buru |
ka-heke |
| |
No, |
this |
hill |
neg-is |
|
|
|
10. |
kage, |
hani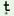 a a |
seta |
ka-heke |
| |
No, |
this |
dog |
neg-is |
|
|
|
11. |
kage, |
a?e |
ka-hiju - tan - a |
| |
No, |
he |
neg-come-tense-cop |
|
|
|
12. |
kage, |
a?e |
aiŋ-a |
haga |
ka-heke |
| |
No, |
he |
I-case |
brother |
neg-tense |
|
| ‘No, he is not my brother’ |
|
It was stated earlier, that the negative marker
ka-occurs with the verb. If it is a simple verb heke, then it occurs as ka- heke. If the verb is with tense marker like seno.jana ‘go-past’, then it
occurs as ka seno jana but not senoka jana. The negative marker always occurs with the verb.
|
13. |
magrai |
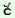 hi hi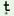 i-rea i-rea |
utura |
ka - om - ta?t - a |
| |
Magray |
letter-case |
reply |
neg - give -asp-cop |
|
| ‘Magray has not answered the letter’ |
|
14. |
babulal |
toraŋ |
bajar-te |
ka-hiju - tan - a |
| |
Babulal |
may |
market-case |
neg-come-tense-cop |
|
|
‘Babulal may not be coming to the market’ |
|
15. |
duar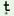 a a |
ka-m |
¸i?i
|
dha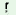 ia- ia-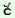 i i |
| |
door |
neg-PT |
open |
can-que |
|
| ‘Can’t you open the door? |
|
4. In the negative questions, the negative
marker occurs at the sentence final position. This may be seen in the
following sentences :
|
16. |
a?e |
duraŋ-ta?t
- a ?e |
| |
he |
sing-asp-cop-PT |
|
|
|
17. |
a?e |
ka-duraŋ-ta?t-a-?e |
|
|
|
18. |
a?e |
duraŋ-ta?t-a-?e-ka |
|
|
|
19. |
alaŋ |
ka-laŋ
|
jom-e-a |
|
We |
neg-PT |
eat - cop |
|
|
|
20. |
alaŋ
|
jom-e-a |
laŋ-ka |
|
We |
eat |
cop-PT-neg |
|
|
|