| 4.5.0. Gender |
|
Like other Centeral Dravidian languages, Abujhmaria has two genders: masculine and non-masculine, both in singular and plural. Masculine gender denotes persons of the male sex and the non-masculine gender denotes persons of female sex, animals, inanimate objects and abstract nouns, In this language noun stems can be classified according to the gender suffix they take:
|
| (a) Nouns ending in masculine suffix. |
| (b) Nouns ending in non-masculine suffix. |
| 4.5.1. Masculine Derivative Suffixes |
| -a:l |
/-a:l  -l -l  -o: -o:  -e:/ -e:/ |
|
/-a:l/ occurs in the following masculine nouns with consonant ending stems.
|
|
gu: -a:l -a:l |
‘dwaft’ |
|
pe:k-a:l |
‘boy’ |
|
pe: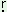 g-a:l g-a:l |
‘boy’ |
|
ko:ry-a:l |
‘bachelor’ |
|
ma:nk-a:l |
‘man’ |
|
ja: -a:l -a:l |
‘immoral person’ |
|
ka:n-a:l |
‘blind-man’ |
|
ko:nd-a:l |
‘dumb person’ |
|
kum-a:l |
‘potter’ |
|
ra:n -a:l -a:l |
‘widower’ |
|
ann-a:l |
‘elder brother’ |
|
ka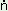 g-a:l g-a:l |
‘poor man’ |
|
ko:p-a:l |
‘milkman’ |
|
meym-a:l |
‘father’ |
|
|
/-l/ occurs in the following masculine nouns ending in a vowel. All of them are borrowed from Indo-Aryan languages.
|
|
da:da:-l |
‘elder brother’ |
|
ba:ba:-l |
‘father’ |
|
ma:ma:-l |
‘mother’s brother, father-in-law’ |
|
ka:ka:-l |
‘father’s younger brother’ |
|
pa:g a:-l a:-l |
‘mad’ |
|
gawli:-l |
‘milkman’ |
|
ka:ti:-l |
‘blacksmith’ |
|
|
In the above and in the earlier examples the final -l is optionally dropped.
|
|