| 10.1.3.1. Subject Deletion in SV |
|
we:ha: |
‘(you) speak, tell’ |
|
han |
‘(you) go’ |
|
hila: |
‘(you) stand’ |
|
| 10. 1. 3. 2. Subject Deletion in SOV |
|
an aru: e:r ta:y |
‘go and bring water’ |
|
pandi: we:hma: |
‘do not tell lies’ |
|
suwa:te: u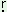 ma: ma: |
‘do not peep in the well’ |
|
| 10.1.3.3. Object Deletion |
| Object is deleted in SO2O1V type. |
|
pe:ki: e:r tata:na: lo:te: hat
‘girl went inside the house to bring water’
|
|
wo:r un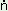 a:la:y e:r tatu:r a:la:y e:r tatu:r
‘he brought water to drink’ |
|
wo:r wo:na: mari:n lo:ho:r
‘he will not send his son’ |
| In the examples given above, object2 is deleted |
|
nima:wo:rkun beske:hi:ti:n?
'when did you give him?' |
| In this example object1 is deleted |
|
| 10.1.3.4. Verb Deletion |
|
In the clause type of subject-subjective complement-verb, the verb is deleted optionally.
|
|
ad pe:ki: |
‘that (is a) girl’ |
|
wo:r ka:na:l |
‘he (is a) blind’ |
|
id bo:na: lo:n |
‘whose house (is) this ?’ |
|
| 10.1.4. Obligatory Elements |
|
The obligatory elements found in these clause types are subject, object, complement and verb.
|
| 10.1.4.1. Subject |
|
Subject is always a single noun or pronoun, a noun or pronoun phrase, an adjective or adjectival phrase used as a noun or verbal noun.
|
|