| -cok occurs after the verb stems ending in -h. |
|
we:h-cok |
‘saying’ |
|
pu:h-cok |
‘blooming’ |
|
te:h- |
‘showing’ |
|
wa:h-cok |
‘boiling’ |
|
ke:h-cok |
‘arresting, obstructing’ |
|
| -jok occurs after the verb stems ending in a nasal. |
|
man-jok |
‘living’ |
|
mam-jok |
‘selling’ |
|
tin-jok |
‘eating’ |
|
han-jok |
‘going’ |
|
in-jok |
‘saying’ |
|
pun-jok |
‘knowing’ |
|
un-jok |
‘drinking’ |
|
| -sok occurs elsewhere. |
|
weli:-sok |
‘wandering’ |
|
ki:-sok |
‘doing’ |
|
kal-sok |
‘stealing’ |
|
gu: -sok -sok |
‘sleeping’ |
|
ki:nj-sok |
‘listening’ |
|
wa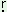 k-sok k-sok |
‘singing’ |
|
pan -sok -sok |
‘making’ |
|
a -sok -sok |
‘cooking’ |
|
a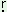 -sok -sok |
‘weeping’ |
|
| 7.10.1.2. Past |
|
Past adverbial participles are formed by adding the suffix -ci: to the verb stems which gives the meaning of ‘having said, having eaten; etc. It has two phonologically conditioned allomorphs -ji: and -si:.
|