| 7.8.5.3. Future Negative |
|
The future negative if formed by the addition of the future tense forms of the auxiliary very a:y- ‘to become’ to the present negative forms.
|
|
The future tense for me of the verb a:y are as follows:
|
| Persons |
Singular |
Plural |
| I |
a:yka:n |
a:yko:m |
| II |
a:yki:/a:yki:n |
a:yki:r/a:yki: |
| III Masculine |
a:ya:n |
a:ya:nu:r |
| III Non-masc. |
a:ya:r |
a:yanu: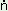 |
|
| 7.8.6. Prohibitive |
|
The prohibitive is formed by adding the prohibitive suffix -ma: to the verb stem.
|
|
Stem ending in -i: change the final vowel into -e: before the prohibitive suffix.
|
The plural suffix - is added to the prohibitive suffix to form plural. is added to the prohibitive suffix to form plural.
|
|
Verb |
II Singular |
II Plural |
|
tin- ‘to eat’ |
tin-ma: |
tin-ma:- |
|
un ‘to drink’ |
un-ma: |
un-ma:- |
|
hu: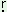 ‘to see’ ‘to see’ |
hu: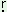 -ma: -ma: |
hu: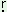 -ma:- -ma:- |
|
han- ‘to go’ |
han-ma: |
han-ma:- |
|
we:h- ‘to say’ |
we:h-ma: |
we:h-ma:- |
|
nil ‘to stand’ |
nil-ma: |
nil-ma:- |
|
hi:- ‘to give’ |
he:ma: |
he:ma:- |
|
| 7.8.7. Imperative |
|
he imperative have two forms and they are second person singular and second person plural.
|
|
Second person singular suffixes are -Ø, -m and -a:.
|
The plural suffix - is added to the singular forms to obtain plural. is added to the singular forms to obtain plural.
|
|
The zero suffix occurs after those verbs ending in -n.
|
| Examples: |
|
Verb |
II Singular |
II Plural |
|
tin- ‘to eat’ |
tin- Ø |
tin-f- |
|
pun- ‘to know’ |
pun-Ø |
pun-f- |
|
man- ‘to live’ |
man-Ø |
man-Ø- |
|
han- ‘to go’ |
han-Ø |
han-Ø- |
|
in- ‘to say’ |
in-Ø |
in-Ø- |
|
un- ‘to drink’ |
un-Ø |
un-Ø- |
|
|