| Examples: |
|
Verb Person |
I and II |
III Masc. and irrationals |
III Feminine |
|
un-
‘to drink’ |
un- -a:k- -a:k- |
un- -a:n -a:n |
un- -a:r -a:r |
|
in-
‘to say’ |
in-d-a:k- |
in-d-a:n |
in-d-a:r |
|
han-
‘to go’ |
han-d-a:k |
han-d-a:n |
han-d-a:r- |
|
ke:nj-
‘to hear’ |
ke:nj-k- |
ke:nj-a:n- |
ke:nj-a:r |
|
ma:ru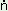 -‘to forget’ -‘to forget’ |
ma:ru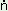 -k -k |
ma:ru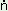 -n- -n- |
ma:ru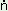 -a:r -a:r |
|
wa:y-
‘to come’ |
wa:y-k- |
wa:y-a:n- |
wa:y-a:r |
|
wark-
‘to speak’ |
wa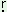 -k- -k- |
wa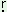 -k-a:n- -k-a:n- |
wa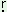 k-a:r k-a:r |
|
|
The future tense suffix is followed by the personal pronominal endigs (Set-e).
|
| Persons |
Singular |
Plural |
| I |
-a:n |
-o:m |
| II |
-i:/i:n |
-i:r/i: |
| III Masculine |
-u:r |
-u:r |
| III Non-masculine |
-Ø |
-u: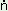 |
|
| 7.8.4. Past-Habitual |
|
The stem is followed by the past-habitual suffix -nd, which, in turn is followed by personal pronominal endings (Set-r).
|
| Persons |
Singular |
Plural |
| I |
-a:n |
-o:m |
| II |
-i:/i:n |
-i:r/i: |
| III Masculine |
u:r |
o:r |
| III Non-masculine |
a: |
a: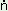 |
|
|
The initial -n of the suffix -nd is dropped when added to the stems ending in a nasal.
|
|
inda:n |
‘I used to say’ |
|
manda:n |
‘I used to live’ |
|
tinda: |
‘it used to eat’ |
After the stem un ‘to drink’ -nd becomes - . . |
|
un a:n a:n |
‘I used to drink’ |
|
un o:r o:r |
‘they used to drink’ |
|
un a: a: |
‘it/she used to drink’ |
|