| 7.8.2. Past Indicative |
|
The past indicative is formed by the addition of the suffix -t to the verb stem. The tense suffix is followed by the pronominal endings.
|
|
Verb |
Past suffix |
Past stem |
|
pan - ‘to make’ - ‘to make’ |
-t |
pan -t- -t- |
|
han- ‘to go’ |
-t |
hat-t- |
|
koy- ‘to pluck’ |
-t |
koy-t- |
|
ke:nj- ‘to hear’ |
-t |
ke:nj-t- |
|
in- ‘to say’ |
-t |
it-t- |
|
mi:y- ‘to bethe’ |
-t |
mi:-t- |
|
mam- ‘to sell’ |
-t |
mat-t- |
|
a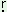 - ‘to weep’ - ‘to weep’ |
-t |
a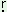 -t- -t- |
|
|
The tense suffix is followed by the pronominal endings (set-2)
|
| Persons |
Singular |
Plural |
| I |
-a:n |
-o:m |
| II |
-i:/i:n |
-i:r/i: |
| III Masculine |
-u:r |
-o:r |
| III Non-masculine |
-a: |
-a: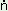 |
|
The past tense suffix has an allomorph - which occurs after the stem un ‘to drink’. The full paradigm is given below: which occurs after the stem un ‘to drink’. The full paradigm is given below:
|
| Persons |
Singular |
Plural |
| I |
u  a:n a:n |
u  o:m o:m |
| II |
u  i: i: |
u  i:r i:r |
| III Masc. |
u  u:r u:r |
u  o:r o:r |
| III Non-masc. |
u  a: a: |
u  a: a: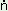 |
|
|
Elsewhere the allomorph -t occurs.
|
| 7.8.3. Future Indicative |
|
The future indicative suffixes are -a:k, a:n and a:r. The are all conditioned morphologically. As a general morphophonemic rule all the verb stems ending in -n take -d before they take the future tense suffix.
|
|
(i) -a:k : It occurs before first and second person pronominal suffixes and after those verbs ending in -i. The allomorph -k occurs elsewhere.
|
(ii) -a:n : It occurs before the third person pronominal suffixes and before the suffixes of irrationals. The allomorph -n occurs after the verb ending in -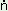 . .
|
|
(iii) -a:r : It occurs elsewhere.
|