| |
|
|
|
7.1.4. The Genitive : The
genitive, as pointed out above, is an attribute. It is not
morphologically marked in Ao except in the case of singular
personal pronouns. The genitive forms of these pronouns have
already been given in section 2.4. It may be recalled here that
the third person singular has special oblique forms only when
the following head noun is non-human. The genitive is therefore
defined by the place of occurence of a noun in relation to the
head noun. One of the relations of a noun that precedes the head
noun is genitive indicating possessor relationship. |
|
|
k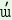 kí
‘my house’
kí
‘my house’ |
|
my house |
| |
m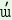  kakàt
‘your (sg) book’
kakàt
‘your (sg) book’ |
|
your book |
| |
pá áz
áz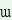 ‘his dog’
‘his dog’ |
|
his
dog |
| |
|
lá tepu
‘her father’ |
|
her father |
| |
nisó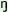 kí
‘man’s house’ kí
‘man’s house’ |
|
man house |
| |
áz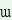 tepen
‘dog’s tail’ tepen
‘dog’s tail’ |
|
dog tail |
| |
uz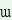 tesep
‘bird’s nest’ tesep
‘bird’s nest’ |
|
bird nest |
| |
| 7.1.5.
Co-ordinate Noun Phrase : |
| |
Co-ordinate noun phrases are formed by joining two or more nouns
or noun phrases with the conjuctive or the disjunctive
particles. The conjunctive particle is /ase /.
This is added before the last of the noun enumerated. /.
This is added before the last of the noun enumerated. |
| |
pá
asé lá
‘he and she’
lá
‘he and she’ |
|
he
and
she |
| |
ipá
nisó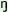 ya
asé
ya
asé pá
pá kí ‘this man and his house’
kí ‘this man and his house’ |
|
this
person
(dem) and
his house |
| |
amenlá, na olá,
benda olá,
benda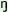 asé asé nokten kohima-yi awó
nokten kohima-yi awó |
Amenla Narola Bendang and Nokden Kohima-to going
|
|
‘Amenla, Narola, Bendang and Nokden are going to Kohima’
|
| |
The
disjunctive particle is /mes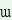  ha/.
This is also added before the last of the nouns enumerated. ha/.
This is also added before the last of the nouns enumerated. |
| |
ká mes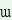  a
aná ‘one or two’ a
aná ‘one or two’ |
| one or two |
| |
tepu mes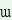  a
capasu ‘father or son’ a
capasu ‘father or son’ |
| father or son |
| |
pá, lá mes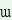  a
ná ‘he, she or you (sg.)’ a
ná ‘he, she or you (sg.)’ |
| he, she or you |
| |
tenak,
tekolak mes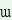  a
teka ‘eye, head or hand’ a
teka ‘eye, head or hand’ |
| eye head or
hand |
| |
| 7.2. The
Verb Phrase : |
| |
|
The predicate phrase in Ao may be a verb phrase, a noun phrase
or an adjective phrase. The internal composition of noun phrases
in the predicate phrase is the same as noun phrases elsewhere.
The verb phrase consists of a verb and certain other
constituents, which precede the verb. The constituents which
precede the verbs are the case noun phrase except the genitive,
nominative and vocative, the adverb and the infinitive. |
| |