| 6.3.4.10 Vb + Vb (Aux.) |
| ki:ttirukke |
‘(I) have torn’ |
| vandirukke:mu |
‘(we) have come’ |
| vandirunde:mu |
‘(we) had come’ |
| 6.3.4.11 Vb + Vb (Aux.) + Cond. |
na anduka: anduka:  ina:kki ina:kki |
‘If (someone) demonstrated (how) to walk’ |
tinRuka:  ina:kki ina:kki |
‘If (someone) demonstrated (how) to eat’ |
| 6.3.4.12 Vb + Vb (Aux1) (Aux2) + Cond. |
ve  imu imu ittirunda:kki ittirunda:kki |
‘If (someone) finished cutting’ |
na anduka: anduka:  irunda:kki irunda:kki |
‘If (someone) demonstrated (how) to walk’ |
| 6.3.4.13 Vb (Aux.) + Vb |
anci vi  u vanda u vanda |
‘After (being) afraid (she) came’ |
vanduvi  u po:ga:ru u po:ga:ru |
‘After (having come) they (are) going’ |
| 6.3.4.14 Vb + Vb (Neg.) |
ėRuddu ve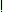 a: a: ina:le ina:le |
‘Did not play throwing’ |
| u:du mekka:le |
‘Did not chew plowing’ |
| 6.3.4.15 N + Vb (Neg.) |
| ve:ru illa:de |
‘without root’ |
| ve:li ille:de |
‘without fence’ |
| 6.4 Imperative |
| Imperative sentences involve only the second person subject which can be deleted optionally. Among the major sentence types, nominal and equational sentences do not have imperative form. Other major sentences have the imperative forms of the verbs. |
ni: ma i i |
‘You (sg.) speak’ |
| you (Sg.) speak |
ni:mu avane pu ivi ivi |
‘You (pl.) hold him’ |
| you (pl.) he (Acc.) - hold |
| Negative imperative |
ni: avane o:  a:da a:da |
‘You (sg.) do not chase him’ |
| you (Sg.) he (Acc.) chase (Neg.) |
nimu avane o:  a:diri a:diri |
‘You (pl.) do not chase him’ |
| you (pl.) he (Acc.) chase (Neg.) |