i) avä a ittä (Decl.) ittä (Decl.) |
‘He bet’ |
| he - bet |
avä a ittä ittä 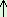 (Interr.) (Interr.) |
‘He bet ?’ |
| ii) mara:tti kuruvi irukku (Decl.) |
‘Bird is there in (the) tree’ |
| tree (Loc.) - bird - there |
mara:tti kuruvi irukku 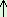 (interr.) (interr.) |
‘Bird is there in (the) tree?’ |
| 6.2 Minor Sentences |
| Minor sentences include mainly vocatives, utterances with exclamation, and short replies. Mostly these sentences will function as independent units or can also be attached to the neighbouring sentences. |
| 6.2.1 Vocative |
| Vocative is formed by the lengthening of the final vowel of the noun (3.8.9). These vocative type is derived from the noun. |
| lasm-i: |
‘Oh ! Lakshmi’ |
| nanc-ä: |
‘Oh ! Nancha’ |
| so:R-e: |
‘Oh ! pigeon’ |
| Another form of vocative expression is also used in Urali. This is effected by using certain vocative elements like e: and o: in the beginning of the utterance. |
| o: lasmi: |
‘Oh ! Lakshmi’ |
e : gun ä : ä : |
‘Oh ! Gunda’ |
| 6.2.2 Exclamation |
| Exclamatory utterances can be attached to some minor sentences also. |
| o: puli ! |
‘Oh, tiger !’ |
| o: agvė! |
‘Oh, (my) mother!’ |
| 6.2.3 Short replies |
| Answer to certain questions can function as a sentence. These answers may be a single word or a phrase. |
| i) Q. adu ä:ru ? |
‘Who (is) that?’ |
| that - who |
| A. ra:mä |
‘Raman’ |
| ii) Q. ava enna se:ga ? |
‘What (is) she doing ?’ |
| she - what - do |
| A. ve:le |
‘Work’ |
| iii) Q. eppRa kala:sinä? |
‘How much he mixed ?’ |
| how much - mixed (P.T.) |
| A. ėtteni |
‘Little bit’ |