| 6.1.1.7 Causative sentence |
| Action pertaining to the subject and the direct object is expressed through the causative sentences. The causative verb in this sentence consistutes the VP. Through the causative sentence, all the syntactic functions of transitives will be satisfied by co-occurring with the object nominals. Another syntactic function would be that of an external causer. That is, the co-occurrence with nominal other than the object nominal is noticed. |
|
masa ä ava ä ava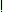 e pa: e pa: isinä isinä |
‘Masana caused her to sing’ |
| masana - she (Acc.) - caused to sing (P.T.) |
avälingändara kattene a ippisugä ippisugä |
‘He cause to beat (the) donkey (through) Lingam’ |
| he - Lingam (Inst.) donkey (Acc.) cause to beat (P.T.) |
| 6.1.2. Complex sentence |
| Complex sentence consists of a simple sentence which constitutes the principal or the main clause of the sentence and one or more subordinate clauses. The main clause of a complex sentence which has the subject and predicate of its own will always occur sentence finally in normal conversation. |
| 6.1.2.1 Temporal element in the subordinate clause |
|
i)aväve:lese:ga:  ikügavü:ndä ikügavü:ndä |
| he - work - when does - down - fell (P.T.) |
‘He fell down while working’ |
ii)bo: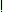 ika: ika: ukkemarave ukkemarave  uga:kku uga:kku |
| Boli - forest (Dat.) - tree - in order to cut |
po:na:  i pilli ma:n a i pilli ma:n a  aäe ka aäe ka  |
| when went - spotted - deer - herd saw (P.T.) |
‘Boli saw a herd of spotted deer when she when to the forest in order to cut the tree’ |
iii) ammäa  anea anea itta: itta:  iu:rugvü iu:rugvü  e e |
| father - elder brother (Acc.) - when bet - village - elder |
ammäne pi ittä ittä |
| father (Acc.) caught (P.T.) |
‘Village elder caught (my) father when (he) bet the elder brother’ |
| Clause analysis |
|
i)aväkügavü:ndä |
‘He fell down’ |
ve:lese:ga:  i i |
‘when (he) was working’ |