| 3.
(p, k, g) + l |
| pl- |
plak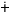 thi thi |
`corriender
seed’ |
| kl- |
kla |
`wed’ |
| gl- |
glas |
`glass’ |
|
|
| 4.
miscellaneous ones |
| ky |
kyį |
`what?’ |
| kr- |
krista |
`christ1’ |
| tr- |
treyin |
`train’ |
 k- k- |
´ku |
`accused’ |
|
|
| Marrison
(1967 : 367) lists the occurrence of a few word-initial clusters,
some of which are not found in the present data. These are kw, khw,
gw and pf,. He has, however, not cited any examples, nor discussed
the occurrence of the word-initial and word-medial clusters. |
| Inter-Vocalic
consonant clusters |
| The
sequence of consonants occurring in the word-medial position may be
defined as intervocalic clusters i.e., sequences of consonants occurring
between two vowels. It may, however be stated that inter-vocalic clusters
are usually split up between the two adjacent syllables, i.e., all
intervocalic clusters have syllable division either before or within
it, as it : |
| -dda |
i-dda |
idda |
`awake’ |
| y-y |
ay-ye-pu |
ayyepu |
`star’ |
| y-w |
ay-wwe |
aywwe |
`leech’ |
|
|
| Since
syllable division is not a phoneme, a sequence of inter-vocalic consonants
continue to be a cluster, even though the consonants of which it is
composed belong to different syllables. |
| Whereas
in the case of pre-vocalic position, the largest number of consonants
that could occur in a sequence is only three, in inter-vocalic position
a sequence of 4 consonants could occur, though only one word having
such a sequence is available in the present data. Even this word has
h (phonetically aspiration) in C2 C4 positions for e.g., |
|
| Whereas
a total of only six types of clusters of C1 C2 C3 were available in
the pre-vocalic position, in the intervocalic position. as many as
28 such clusters are available. What is common in both these positions
is the occurrence of h as one of the elements, for instance, in the
pre-vocalic position h occupied C3 position in 4 types and C2 position
in the remaining two types whereas barring a few instances of clusters
of homorganic consonants and a few other clusters like-kly- that do
not have a h, the C1 C2 C3 clusters in intervocalic position have
h either in C2 or C3 position. Even some of the homorganic consonant
clusters like mph nth etc. have h in C3 position. When a cluster has
C1 C2 sequence sequence, the maximum number of consonants that could
form a sequence is only two, except when the C3 is a h. Another feature
that is common in both these positions is the occurrence of m in the
C1 position. In the pre-vocalic position, four out of the six types
had m in C1 position and in three types the other nasals occur. For
the sake of convenience, sequences of C1 C2 C3 consonants occurring
in intervocal position are sub-grouped into 9 sub-types. These are
given below. |
| 1.
m+ (p,t, c, k, q, n, l) +h |
| mph |
amphóbņ |
`hearth’ |
| mth |
k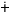 mthe mthe |
`sacredness’ |
| mch |
ak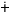 mcha mcha |
`soft
ground’ |
| mkh |
amkhu |
`dust’ |
| mqh |
Khumqho |
`heat
(n)’ |
| mnh |
amnhi |
`fibre’ |
| mlh |
amlhi |
`lean’ |
|
|
| 2.
(y, l, m, p, k, s) + kh |
| ykh |
aykhu |
`egg’ |
| lkh |
alkhok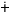 z z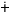 |
`stockings’ |
| mkh |
amkhu |
`dust’ |
| pkh |
apkhu |
`leg’ |
| kkh |
lakkhą |
`restricted’ |
| skh |
askhņ |
`umbrella’ |
|
|
| 3.
K+ (t, m, l) + h |
| kth |
xśktho |
`provoke’ |
| kmh |
akmho |
`corpse’ |
| klh |
yeklha |
`notification’ |
|
|
| 4.
(k, s, j) + Ih |
| klh |
yeklha |
`notification' |
| slh |
aslho |
`in
the water’ |
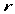 lh lh |
a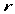 lhu lhu |
`dinner’ |
|
|
|