the instrumental
with the inanimate beings. A VP with a verb in either transitive or intransitive
construction could have anoun in the sociative relation. The postposition
sas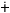 marks the sociative case
relation. marks the sociative case
relation. |
| Since the
sociative relationship is marked overtly, a noun/pronoun in the sociative
has relatively some freedom of occurrence within the VP, i.e., it may be
pre or post-posed to an adverb and/ or a NP in the accusative relation,
as in: |
| |
{asi
pasas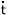 } } |
|
| niye
|
|
cúwe `I ate meat with him’ |
| |
{pasas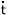 asi}
asi} |
|
|
|
| Structurally,
the noun/pronoun in the sociative is a verb complement. |
| |
| 5.
Instrumental |
| The instrumental
case relation expresses the material cause of an event, i.e., and animate
object used for doing a particular work. In other words, the instrumental
case occurs with the nouns inanimate being class and in Sema, this relationship
of a noun/pronoun is expressed with a noun / pronoun showing the accusative
relation with the verb of the VP. This automatically requires the verb to
be in the transitive construction. Structurally, a noun/pronoun in instrumental
relation is a verb complement. Pe is the case marker for the instrumental
relation as in : |
ino
|
ak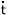 s s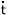
|
lakhì
|
pe
|
li
|
`I |
beat
|
her |
with |
a |
stick’ |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 6 |
1 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
ino |
is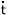 l l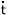
|
ak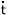 s s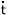
|
lakhì
|
pehequì |
`I |
beat
|
her |
today |
with |
a
stick’ |
|
|
Passive agent
: When the sentence is in the passive, the agent may or may not be expressed
overtly. When the passive agent is not expressed, the NP in the instrumental
case relation may be postposed to the NP in the accusative and/or the adverb
in the VP, or may even occur as the first word in the sentence, as in :
|
liye
aki i
lakhì pe isi c i
lakhì pe isi c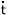 wya
} wya
} |
|
|
| |
|
`she
was tied with a rope’. |
aki i
lakhì pe isi liye c i
lakhì pe isi liye c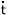 wya
} wya
} |
|
|
|
|
| When the
agent is expressed it may occur any where between the agent and the verb,
as in : |
| |
liye
ino isi aki i
lakhì pe } i
lakhì pe } |
|
`she
was tied by me with a |
| |
|
|
| cöwya
} |
|
rope
today’. |
|
|
| 6.
Local function |
We
now consider the so-called local functions of the case as applicable t
this language. The term local would include, temporal as well as spatial
distinctions. In the system of local, a three way oppositional feature
is found, viz., to a person, from a place or person and to/in/into an
inanimate object. |
It
is, however, pertinent to note here that in Sema the primary local distinction
(viz. to/in/at) are combined with reference to the animate/inanimate feature
of the object of the verb, i.e., the allative marker is available only
when the noun functioning as the object refers to an animate being. If
it refers to an inanimate being, the distinctions of to. in, at all merge
into a single form viz., to, which has been designated as locative case
marker. The locative marker lo does not occur with nouns referring to
animate beings. Within the locative, there are some minor differences
having three dimensions, viz., vertical, horizontal and relative location
of an object to another object. A brief discussion of all these points
follow. |
| 6-a.
Allative |
The allative case relationship refers to the destination/direction to
which the verb and the subject of the sentence moves. The case marker
is law. As far as the Sema language is concerned, this case marker is
used only when the destination/direction is a noun referring to an animate
being, as in : |
| ino
palaw úwe |
`I
went to him’ |
| ino
olaw úwe |
`I
went to you’ |
| ino
amsilaw úwe |
`I went to the buffalow’ |
| paye
isoulaw úwe |
`he
had gone to my friend’ etc. |
|
|
When
the destination/direction is a noun referring to an inanimate being the
locative case marker is used as in : |
ino
|
alhikì
|
lo
|
úwe |
|
`I |
went
|
to |
the |
shop’ |
|
|
1 2 |
3 |
4 |
5 6 |
|
(lit. |
I |
business
|
house |
in |
go |
past) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
i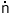 uqóye uqóye
|
akiphikìlo
|
úwe
|
|
`my
|
daughters
|
have
|
to |
go |
the |
school’ |
anulino
|
a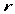 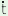 lulo lulo
|
i e e |
|
|
children
|
come
|
to |
the |
garden’ |
|
|
|
|
| 6-b.
Ablative |
The
ablative case is associated with the removal (Lyons 1974: 289). Lyons
(1974 : 290) further states that the ablative has a variety of functions
including that of marking the instrument with which something is done.
In addition, it has various adverbial functions with respect to the distinctions
of place and time. In Sema, it has a limited function of indicating the
place/location from which a person/object is removed. lawno, which seems
to |