| to
obtain respectively the masculine and feminine genders. A few illustrative
examples are given below: |
| `shop
keeper’ |
alhizeu
(common gender) |
| `alhizepś
(masculine) |
`alhizelyś
(feminine) |
| `servant’ |
aqeu
(common gender) |
| `aqepś
(masculine) |
aqelyś
(feminine) |
|
|
| This
type of using separate gender suffixes for differentiating the males
and females engaged in a profession, however is not available with
all the nouns referring to different professions, for instance. |
|
| Never
takes any gender marker. In addition, the nouns referring to the human
beings including the kinship terms do not take any gender marker,
for example : |
| itimś |
`grown
up boys and girls’ |
| timģ |
`man’ |
| totimģ |
`woman’ |
| ilimģ |
`lady’ |
| apś |
`son/boy’ |
| alyś/lyś |
`maid’ |
a a a |
`daughter/girl’ |
| afo |
`elder
sister’ |
| amu |
`elder
brother’ |
| amł |
`daughter-in-law’ |
| ama |
`son-in-law’ |
a u u |
`maternal
uncle’ |
| ani |
`maternal
aunt’ |
| acepu |
`younger
sister (direct) |
| apeś |
`brother’
etc |
|
|
| Inanimate
being class of nouns (Nina class of nouns). - All the nouns referring
to the inanimate beings including the parts of body of the human and
animate non-human being which belong to the Nina class of nouns also
do not show any gender marker as in : |
| asi |
`meat’ |
| axamnu |
`flower’ |
| akģ |
`house’ |
| kaku |
`book’ |
| alu |
`field’ |
as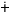 nika nika |
`leaf’ |
| aphu |
`village’ |
| au |
`hand’ |
| apukhu |
`foot’
etc. |
|
|
| Birds
and animals :- The nouns raring to the birds and animals in Sema belong
to the animate non-human being class of nouns (NnH class). These nouns
show a three-way opposition in gender. These are (i) a common gender
referring to both the male and female beings, (ii) a masculine gender
referring to the male beings, and (iii) a feminine gender referring
to the female beings. Of these, whereas the common gender does not
take any gender suffix i.e. the base form the noun itself indicating
the common gender, the masculine and feminine genders are obtained
by suffixing separate gender markers to the base form of the noun.
The nouns referring to the female beings show a further two-way opposition
in gender for indicating whether or not the female beings has/had
issues1. Given below are the examples of different sub-class of nouns
referring to the animals and birds along with the gender suffixes
each of these sub-classes takes. |