|
|
 as qalamčik as qalamčik
|
ńosa? |
| 1
2 3 |
4 5 |
Did I purchase |
a pen ? |
| 5 1
4 |
3 2 |
kho sirinagarla |
čhača:in |
| 1
2 3 |
4 5 |
he will go |
to Srinagar |
| 1
5 4 |
3
2 |
kho sirinagarla |
čhača:lna
? |
| 1 2
3 |
4 5
6 |
will he go |
to Srinagar ? |
| 5+6 1 4 |
3
2 |
|
The suffix -a occurs with the verb
category alone and not with any other grammatical category. The
change in the structure can be shown as |
NP X Y Vb ® |
NP X Y Vb-a |
where x and y may be null or nonnull. |
|
This rule attaches -a to the verrb category. The
sentence is rejected as ungrammatical if the suffix -a is added
to other category than the verb. |
 as
isa as
isa |
čaqs |
| 1
2 |
3 |
I broke |
(the) glass |
| 1 3 |
2 |
 as
isa as
isa |
čaqsa ? |
| 1
2 |
3 4 |
Did I break |
(the) glass ? |
| 4 1
3 |
2 |
*  asa
isa
čaqs ? asa
isa
čaqs ? |
*  asa gadia čaqs
? asa gadia čaqs
? |
|
Similary the suffix -a cannot occur with both the verb and noun
phrase categories. Such sentences are not accepted as
grammatical. |
 asa
isa
čaqs ? asa
isa
čaqs ? |
*khosa oqbu
silsa ? |
*khos oqbua
silsa ? |
|
4.2.5.2.
|
Wh-Type |
If the noun phrase in the subject position is human, then su
will occur as the interrogative word replacing the subject noun
phrase. This may be shown as |
NP X Y Vb ® |
Su X Y Vb |
where x and y may be null or nonnull elements |
and NP is specified as (+Human). |
kho r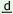 amo amo
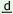 uk uk |
| 1 2
3 |
she is beautiful |
| 1 3
2 |
su r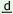 amo amo
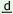 uk ? uk ? |
| 1 2
3 |
who is beautiful ? |
1 3
2
|
|