|
|
I |
closed |
(the) door |
| 1 |
3 |
2 |
phru |
guls |
|
| 1 |
2 |
|
(the) child |
moved |
|
| 1 |
2 |
|
 as as |
phru |
skuls |
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
I |
moved |
(the) child |
| 1 |
3 |
2 |
laqcukspu |
gel |
|
| 1 |
2 |
|
(the) tree |
fell |
|
| 1 |
2 |
|
 as
laqcukspu as
laqcukspu |
zgels |
|
| 1 2 |
3 |
|
I made |
(the) tree |
to fall |
1 3
|
2
|
3
|
|
In all these examples,
we find the prefix s- being added to the intransitive bases. If
we name these constructions as direct causation, then we can
label the constructions with cuk as indirect causation. cuk is
also added to the verb stems in order to express causative
constructions.
|
 as as |
pikčarčik |
I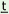 as as |
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
|
I saw |
a picture |
|
|
| 1 3 |
2 |
|
|
 i i
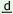 o:spu o:spu |
 a
oqbuik a
oqbuik |
I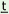 acuks acuks |
|
| 1 2 |
3 4 |
5 6 |
|
I made |
my friend |
to see |
(the) book |
| 1 6 |
3 2 |
5 |
4 |
 as
zgo as
zgo |
phes |
|
|
| 1 2 |
3 |
|
|
I opened |
(the) door |
|
|
| 1 3 |
2 |
|
|
 as
mia as
mia |
zgo phecuks |
|
|
| 1 2 |
3 4 |
|
|
I made |
(the) man |
to open |
(the) door |
1 4
|
2
|
4
|
3
|
|
4.2.4.
|
Comparative Constructions |
|
The degree of comparison
is expressed by the use of bacik in Purki. This may be
considered as equivalent to { er } than
in English. Consider the following sentences. |
{ more }
|
| gula:p |
ya:sminbacik |
r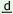 amo amo |
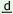 uk uk |
|
| 1 |
2
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
rose is |
more |
beautiful |
than |
jasmine |
| 1
5 |
3 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
 as as |
kherabacik |
ri mo mo |
duk |
|
| 1 |
2
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
I am |
taller |
than you |
|
|
| 1 5 |
4 3 |
3
2 |
|
|
 i ka:rpu i ka:rpu |
khoe |
ka:rbacik |
rgya:la |
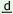 uk uk |
| 1 2 |
3 |
4 5 |
6 |
7 |
my car |
is better |
than his |
car |
|
1 2
|
7 6
|
5
4
|
3
|
|
|