|
|
The distribution of duk any yot is
based on the co occurrence restriction of tense also. If the
tense is future tense, then duk occurs in all the places.
The negative marker mi occurs and not min.
|
NP X Y Vbr + Pr. Pl. +
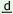 uk + Fut
® uk + Fut
®
|
NP X Y Vbr + Pr. Pl. + mi +
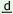 uk uk |
|
x and y may be null or nonnull. |
 as as |
zbrin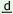 uk uk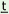 uk uk |
|
| 1 |
2 3 4 5 |
|
I will |
be writing |
|
| 1 5 |
4 2 3 |
|
 as as |
zbrinmin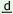 uk uk |
|
| 1 |
2 3 4 5 |
|
I will |
not be |
writing |
| 1 |
4
5 |
2 3 |
kheras |
zbrinmin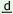 uk uk |
|
| 1 |
2 3 4 5 |
|
you will |
not be |
writing |
| 1 |
4 5
|
2 3 |
khos |
zbrinmi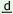 uk uk |
|
| 1 |
2 3 4 5 |
|
he will |
not be |
writing |
1
|
4 5
|
2 3
|
|
4.2.3.
|
Causative Constrauctions
|
The prefix s- is added
to the intransitive base in order to derive the transitive verbs
(refer to 3.2.1.2.). All the transitive verbs are not causative
but all the causatives when they are derived from the
intransitive bases by adding prefix -s are transitive verbs.
|
In the process of
causativization, the subject noun phrase of the intransitive
verb becomes the object noun phrase of the transitive verb. This
is a syntactic process that is significant in the causative
construction. This is claimed to be a universal feature of human
language. The examples from Purki support this claim further.
|
| čhu |
xolat |
|
| 1 |
2 |
|
(the) water |
boils |
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
 as
čhu as
čhu |
skols |
|
| 1
2 |
3 |
|
I boil
|
(the) water |
|
| 1
3 |
2 |
|
kiti |
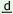 ulat ulat |
|
| 1 |
2 |
|
(the) boat |
sails |
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
 as
kiti as
kiti |
strulat |
|
| 1
2 |
3 |
|
I sail |
(the) boat |
|
| 1 3 |
2 |
|
zgowu |
dums |
|
| 1 |
2 |
|
(the) door |
closed |
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
 as zgowu as zgowu |
z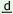 ums ums |
|
1
2
|
3
|
|
|