| 4.13.2.
Imperative : |
| It indicates
commands, instructions or requests. The subject of the imperative,
which must be in the second person, is optional. |
| 1.
Simple imperative : |
It shows a two way opposition viz., motion verbs take /-ka /
or /-na /
or /-na / as imperative
marker when the action is directed towards the speaker, and when the
action is directed away from the speaker, the marker is either /-ka / as imperative
marker when the action is directed towards the speaker, and when the
action is directed away from the speaker, the marker is either /-ka -ku/
or /-la -ku/
or /-la -ku/. The
stative verbs take /-t -ku/. The
stative verbs take /-t -ka/ to mark
imperative mood, the second syllable /-ka/ is optional. -ka/ to mark
imperative mood, the second syllable /-ka/ is optional. |
| Motion
verbs : |
i)
VR + -ka -na -na
|
ii)
VR + -ka -na -na -ku
-ku |
|
iskul-pė
|
g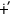 -ka -ka
|
‘Go to school’
|
|
school towards
|
go imp
|
|
iskul-d kke kke
|
g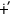 -ka -ka
|
‘Go from the school’
|
|
school from
|
go imp
|
|
iskul-l kke kke
|
gi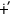 yį-la yį-la -ku -ku
|
‘Come from the school’
|
|
school from
|
go-imp
|
|
|
kitabdėm
|
b m-lat-na m-lat-na -ku -ku
|
‘Bring back the
books’
|
|
book
|
bring back imp
|
|
|
|
la g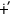 yį-lat-na yį-lat-na -ku -ku
|
‘Go home and come
back’
|
|
home go imp
|
and come back imp
|
|
|
|
| Stative
verbs |
VR +
t + ka + ka |
|
dś
|
t (ka) (ka)
|
|
‘Sit down’
|
ag m m
|
k
|
lś-t (ka) (ka)
|
‘say something’
|
|
word
|
one
|
speak imp
|
|
(n ) )
|
isim
|
lįsa-t (ka) (ka)
|
‘Lift it up’
|
|
(you)
|
this
|
bring up imp
|
|
|
isim
|
gągįp-t (ka) (ka)
|
|
‘Holt it’
|
|
this
|
hold imp
|
|
|
|
apin
|
d -t -t (ka) (ka)
|
|
‘Eat food’
|
|
food
|
eat imp
|
|
|
|
|
| 2.
Polite imperative : |
| It expresses
request. It takes /-pen/ after /-t¨/.
|
| VR + -t¨
+ -pen |
|
apinė
|
d¨@t¨-pen
|
‘Please take the
food’
|
|
food
|
eat+ tense imp
|
|
|
galłkgįs¨r
|
b¨@m-t¨-pen
|
‘Please bring the
dress’
|
|
dress
|
bring t imp
|
|
|
is¨pė
|
g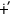 -t¨-pen -t¨-pen
|
‘Please come here’
|
|
here
|
come t imp
|
|
|
asi
|
b¨@mlat-ku-pen
|
‘Please bring back
water’
|
|
water
|
bring back imp
|
|
|
|
| 4.13.3.
Command : |
| It specifies
the necessity and obligation for the action to be performed. Depending
on the obligation, three types of commands can be distinguished. |
| 1.
Instruction |
| VR + t-ika |
|
kį-t¨-ika
|
‘See it (because
it is essential)’
|
|
see t mood
|
|
|
p¨ri-t¨-ika
|
‘Read it (it is
necessary)’
|
|
read t imp
|
|
b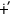 leNkaN-t¨-ika
leNkaN-t¨-ika
|
‘He must appear
(it is wanted)’
|
|
he appear t mood
|
|
|
|
| 2.
Lnjunction |
| i)
VR + t¨-ruN
(present) |
| ii)
VR + pye-ruN (future) |
| iii)
VR + ka-ruN (past) |