n
|
g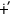 -sa-til(a)-du-laN -sa-til(a)-du-laN
|
‘Surely you will
be climbing’
|
|
you
|
go up asp t
|
|
d py py dė dė
|
y k-pįk-til(a)-duye k-pįk-til(a)-duye
|
‘Surely, the thief
will be dis-appearing’
|
|
the
|
thief disappear
asp t
|
|
|
|
| 4.12.3.
Perfective : |
| It indicates that the
action has already been completed. It shows a two way apposition for
time. |
| 1)
Present perfective : |
| The marking
is optionally by the suffix /-t/ ~ /-tak/. The order of occurrence
is often the verb root before the tense marker. |
|
|
apinėm
|
d -to/-tak-b -to/-tak-b
|
‘I have eaten food’
|
|
I
|
food
|
eat t
|
|
|
bļ
|
p nėdėm nėdėm
|
kį-tak-b
|
‘He has been a thief’
|
|
he
|
thief
|
asp-t
|
|
|
bu-lu
|
muruk nėm nėm
|
lį-tak-b
|
‘They have brought
money’
|
|
they
|
money
|
bring asp t
|
|
|
|
iskul
|
g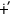 -ka-b -ka-b
|
‘I have gone to
school’
|
|
I
|
school
|
go t +asp
|
|
|
|
| 2)
Past perfective : |
It takes
/-tuN (duN)/
as perfective marker and past tense marker /-ab /. /. |
(1)
VR + -tuN + ab
|
|
|
apinė-m
|
|
‘I had eaten food’
|
|
I
|
food
|
eat-asp t
|
|
|
bi
|
p nėdėm nėdėm
|
kį-du -ab -ab
|
‘He had seen the
thief’
|
|
he
|
thief
|
see asp t
|
|
|
|
| (2)
To express remote perfective, the verb takes the following shape. |
| VR + tak
+ ab¨ |
|
|
apinėm
|
d -ta-gab -ta-gab
|
‘I had eaten food
(long back)’
|
|
I
|
food
|
eat asp t
|
|
|
agerė
|
ger-ta-gab
|
|
‘Labourer had worked
(long back)’
|
|
labourer
|
work t +asp
|
|
|
|
bļ
|
k dėm dėm
|
kį-ta-gab
|
‘He had seen the
boy’
|
|
he
|
boy
|
see t +asp
|
|
|
|
| 4.13.
Mood : |
| Mood
expresses the attitude of the speaker to the action or state denoted
by the verb: real, intended, demanded or desired. |
| For purposes
of description, words here include verb modalities as well. |
| 4.13.1.
Declarative : |
| The action
of the verb indicates a factual statement. It occurs with all the
tenses. There is no special marker for this mood. |
ne -dė -dė
|
dumļt
|
tuk-su-du
|
‘The woman is combing
her hair herself’
|
|
woman the
|
hair
|
comb self t
|
|
|
mļbi-ė
|
k ka ka -kiri-dėm -kiri-dėm
|
d b b -dagai -dagai
|
‘The priest was
feeding the children’
|
|
priest the
|
child pl. to
|
feed t
|
|
|
bļ
|
arig-l -pe -pe
|
g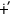 -ye -ye
|
‘He will go towards
the farm’
|
|
he
|
farm towards
|
go t
|
|
|
|