| Following
are the characteristics of adjectives. |
| i)
Adjectives are both free and derived |
| ii) Adjectival
are only derived. |
| iii)
Adjectives are not inflected for gender and number. |
| Examples
- |
| Free
forms - |
apļ
|
‘all’
|
|
isi
|
‘this’
|
įr
|
‘truth’
|
b tt tt
|
‘great’
|
|
|
| Derived
forms - |
miglśnė |
blink |
| (amid eye,
alśmnė round) |
|
| aipė |
good |
| (ainam virtue,
pė at) |
|
|
|
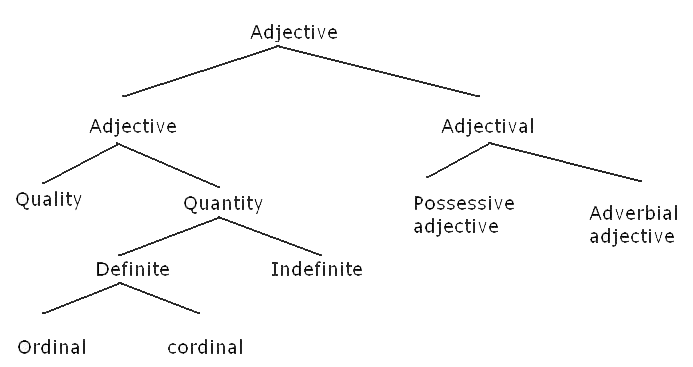
| 2.1
Following is the chart which shows classes and subclasses of adjective. |
 |
| Examples
- |
az nė nė
|
d luė luė
|
|
|
‘small village’
|
|
small
|
village
|
|
|
|
|
bļ
|
ut dąk
|
|
|
‘he is tall’
|
|
he
|
tall is
|
|
|
|
k
|
dė
|
rśbė
|
dąk
|
‘the boy is deaf’
|
|
boy
|
the
|
deaf
|
is
|
|
|
ainė
|
k
|
dė
|
|
‘the good boy’
|
|
good
|
boy
|
the
|
|
|
|
battįnė
|
ami
|
|
|
‘great man’
|
|
great
|
man
|
|
|
|
ke_ m
nė m
nė
|
mukkan
|
kiridė
|
|
‘the dark clouds’
|
|
dark
|
cloud
|
pl
|
|
|
|
zėgėnė
|
annė
|
dė
|
|
‘the green leaf’
|
|
green
|
leaf
|
the
|
|
|
|
kąnkaė
|
d lu lu
|
k
|
|
‘one beautiful village’
|
|
beautiful
|
village
|
one
|
|
|
|
|
| 2.2
Adjectives of quantity : |
| They
denote measurement and stand for the responses to the questions ‘how
much’ and ‘how many’. When a phrase has both qualitative and quantitative
adjectives, the qualitative adjective precedes the noun and the quantitative
follows the noun. |
| Examples
: |
ką kanė kanė
|
ami
|
anńid
|
‘two beautiful men’
|
|
beautiful
|
man
|
two
|
|
|
zėgėnė
|
annė
|
az snė snė
|
‘few green leaves’
|
|
green
|
leaf
|
few
|
|
|
|
| There
are two types of quantitative adjectives - |
| (a)
Indefinite |
| (b)
Definite |