  kke kke |
mėl kke kke
|
kįnamk
|
|
lit. "yesterday
my seen boy"
|
|
my
|
yesterday
|
seen boy
|
|
The boy whom I saw
yesterday
|
|
bļ-kke
|
yubt mamėm mamėm
|
|
duyė
|
lit. "his not
sleeping to I here will sit"
|
|
his
|
sleeping to
|
I here
|
sit t
|
Till he sleeps,
I will sit here.
|
|
apin
|
d d d m m
|
ag m m
|
lśy ka
ka
|
lit. "food
eating to do not speak"
|
|
food
|
eat to
|
word
|
say neg. imp
|
While eating food,
do not speak.
|
|
bļkke
|
g m m namdė namdė
|
ar
|
|
|
|
His
|
coming
|
is true
|
|
|
|
|
| 1.3.2.1
Subordinate clause with relators : |
|
bļ
|
ayinė
|
amik
|
dėmpila
|
|
bļm
|
ayipė
|
medak
|
|
he
|
good
|
man a
|
so
|
I
|
him
|
good
|
think
|
|
|
| He (is)
a good man, so I like him. |
mast r r
|
dė
|
g -ma-ye -ma-ye
|
ėmna
|
bļlś
|
da-ga-i
|
|
teacher
|
the
|
go not tense
|
like
|
he
|
say t +mood
|
|
|
| ‘The teacher
won’t go like this’, he said. |
sėk m m
|
|
s gąp gąp
|
du ai ai
|
|
whom
|
I
|
catch
|
past
|
|
|
Whom I caught.
|
|
|
 d d kke kke |
yubla
|
|
|
|
now
|
sleep
|
|
|
|
|
Now sleep.
|
|
|
g gėla gėla
|
 d d kke kke |
yubla
|
|
|
having gone
|
now
|
sleep
|
|
|
|
Having gone, then
sleep.
|
|
|
|
|
k dė dė
|
kabdu
|
teu
|
bu-lu
|
ap 
|
bļ-ma-ye
|
|
child the
|
weeping
|
yet
|
they
|
wine
|
give neg t
|
|
|
| The child
is weeping, yet they won’t give (him) wine. |
  kke kke |
g gnė gnė
|
amidė
|
g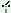 yadak yadak
|
|
my
|
called
|
man
|
went
|
|
|
| lit. "my
called man went" |
| The man
whom I called went away. |
|
1.4. Sentence level |
| A Missing
sentence is an isolated utterance together with its own characteristic
intonation pattern. A sentence without its intonation pattern is a
base sentence. A base sentence in Missing is simple, affirmative,
declarative and active. Other syntactic constructions are derived
from the base sentence. Thus a base sentence serves as the input and,
after applying various transformational rules, such as negative transformation,
interrogative transformation, etc., we get output strings. The usual
pattern of the base sentence in Mising is - |
| subject
+ object + verb |
| A sentence
in Missing is basically of two types i.e., major sentence and minor
sentence. |
| 1.4.1.
Major sentence : Sentences which are well formed are major sentences.
A major sentence has the following basic structure - |
| Base -
An independent clause forms the base of a major sentence. In Missing,
a verb is the only obligatory form to constitute a sentence, but such
a sentence won’t be called a major sentence. Therefore, subject and
object forms are also nuclear to form a major sentence. So, for a
major sentence, subject, object and verb are nuclear functional forms,
while temporal, locationals, etc., are optional. In other words, the
minimum requirement for a major sentence is NP + VP. |
| Major
sentences are of three types - (1) Simple (2) Complex and (3) Compound.
|