|
(iii)
|
+ Adj P
|
+ VR
|
+ suffix(es)
|
|
|
ayļpė
|
mė-dagai
|
(someone) thought
well
|
|
|
well
|
think tense
|
|
|
(iv)
|
Adv P
|
+ VR
|
+ suffix(es)
|
|
|
k l l pė pė
|
g ye
ye
|
Where will (you)
go?
|
|
|
where
|
go tense
|
|
|
(v)
|
VR
|
+suffix
|
+Neg.
|
|
|
g
|
ka -ku-ma -ku-ma
|
Do not come back
|
|
|
go
|
mood not
|
|
|
|
|
1.3. Clause level Construction : |
| Clause level constructions
are higher than phrase level. Phrases combine into the larger structure
of clause. A clause conveys a complete message. In simple sentence
construction, clauses and sentences coincide entirely, but there is
a basic difference between a clause and a sentence. Sometimes, a verb
phrase, say, having only one word, stands as a complete sentence,
while a clause is a combination of phrases and, hence, it does not
possess this characteristic. a clause must have a subject and only
one predicate. The predicate may be a finite verb phrase, indicating
time, purpose, location of event and manner of the action indicated
by VP. |
| Clauses
are of two types - |
| (a)
Independent clause |
| (b)
Dependent clause/Subordinate clause |
| 1.3.1.
Independent clause : Such a clause can stand alone as a major sentence.
The independent clause has three subgroups- |
| (i)
VP containing one or two NPs. |
|
|
rutė
|
k m m
|
d -du -du
|
I am eating bread
|
|
I
|
bread
|
to
|
eat t +Asp
|
|
n kkeawėdė kkeawėdė
|
bu-lum
|
kitabdėm
|
bi-du
|
Your son is giving
them a book.
|
|
your son
|
them
|
book to
|
give+t
|
|
|
subject
|
NP1
|
NP2
|
|
|
|
|
| (ii)
VP without NP |
|
|
g -d -d
|
|
I go.
|
|
I
|
go t
|
|
|
|
sub
|
VP
|
|
|
|
|
arig -l -l pė pė
|
g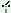 -d -d
|
I go to field
|
|
I
|
field at
|
go t
|
|
|
sub
|
adjunct
|
location
|
|
|
|
| (iii)
Copulative clause : |
| If only
a copula verb occurs in the clause and conveys complete meaning, it
is known as a copulative clause. |
|
bļ
|
isi-l
|
lu
|
|
He is here
|
|
he
|
here
|
copula
|
|
|
|
sub
|
location
|
|
|
|
|
sidė
|
iki
|
aumk
|
du
|
There are three
dogs
|
|
there
|
dog
|
three
|
copula
|
|
|
location
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1.3.2.
Subordinate clause : |
| A
subordinate clause is that which cannot stand alone as a major sentence.
Such clauses need realtors to be embedded within an independent clause.
When the relator is removed, a subordinate clause may become an independent
clause. |
| In
Missing, subordinate clauses are mainly sequential clauses. Such a
type of clause is either adverbial or adjectival. |