| VR
+ y ± ka |
lś-y -(ka) -(ka)
|
|
‘Do not say’
|
|
say neg imp
|
|
|
s m m
|
d -y -y -(ka) -(ka)
|
‘Do not eat this’
|
|
this
|
eat neg imp
|
|
|
isim
|
lįsa-y -(ka) -(ka)
|
‘Do not lift it
up’
|
|
this
|
lift up neg imp.
|
|
is pė pė
|
g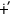 -y -y -pen -pen
|
‘Please do not come
here’
|
|
here
|
go neg imp.
|
|
|
|
| 4.15.10.
Interrogative Negative : |
|
The negative particle is preceded by the interrogative particle /-n/,
/-a/ and /-i/. In probability mood, in interrogative negative
sentences, /-zi/ is added as the probability interrogative particle. |
n
|
unkue
|
g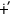 -t -t -ma-n
? -ma-n
?
|
‘Why didn’t you
go?’
|
|
you
|
why
|
go t neg int
|
|
|
|
ger-t -ma-n
? -ma-n
?
|
|
‘Don’t I work?’
|
|
I
|
do t neg int
|
|
|
n
|
unkue
|
g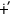 -sa-ma-Na-n -sa-ma-Na-n
|
‘Why are you not
climbing up?’
|
|
you
|
why
|
go up neg t int
|
|
|
abu
|
g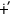 -ma-ye-a
? -ma-ye-a
?
|
|
‘Won’t father go?’
|
|
father
|
go neg t int
|
|
|
|
|
 l l pė pė |
g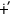 -lama-ye-zi -lama-ye-zi
|
‘May I not go there?’
|
|
I
|
there
|
go neg mood-t int
|
|
bļ edi-l
|
g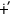 -ma-ye-zi -ma-ye-zi
|
  kin-ma-n
kin-ma-n |
‘Don’t I know when
he would come?’
|
|
he when
|
come neg t int
|
I know neg int
|
|
kitabk bļ
bļ
|
|
  kin-ma-n
kin-ma-n |
‘I do not know where
he keeps his book’
|
|
book he
|
where keep int
|
I know neg int
|
|
|
|
|
5. Word Formation |
| 5.0.
Word level constructions are morphological, i.e., the way in which
the morphemes are put together. In Mising, it is done by inflection
and derivation. The noun derivation is through (1) affixation
- affixes are bound forms and they occur only with free forms; (2)
reduplication - the process of repetition of the whole or a
part of the base; (3) suppletion in which the entire
base is replaced by another base, eg., copula /-duN/
to be replaced by /-dak/; and (4) compounding. Free forms can
occur alone and are capable of conveying complete meaning. Bound forms
have some meaning, which is manifested only when they occur with some
other free form(s). On the basis of the privileges of bound forms
combining with free forms and various permutations and combinations
of free forms, the following word types can be posited. |
| (a)
Simple word - It is a free fomr and enters into syntactic constructions
alsone. |
| (b)
Derived word - It consists of a free form and a suffix. |
| (c)
Compound word - It consists of two or more free forms with or
without suffixes. |
| 5.1.
Derivation |
In
Mising, only the outer layer of formative-elements define the major
form classes. Derivational suffixes occur in the word-final position,
and are capable of changing the form class and distinguishing different
form classes. By suffixing the derivative suffix /-ne/ to the verb
root, the form class of noun and adjective can be derived; only by
looking at the slots in which such a derived form occurs, one could
state whether a derived form is a noun or an adjective - nouns can
also be derived from the verbs by suffixing /-tad/, /-Nk /,
/-p /,
/-p /
and /-nam/. a brief discussion of these follows /
and /-nam/. a brief discussion of these follows |