the agent and the actual performer is
the executor. A detailed explanation of these terms is given in the chapter
on case.
|
There are two causative suffixes, /-bo/
`because’ used when the executor is the subject and /-syig/ `cause’ used
when the agent is the subject. These two are morphologically in contrast
with the configuration when the agent and the executor are co referential. To
exemplify,
|
| (182)
|
/h 1
tap 1
tap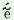 2 thįdebo3/ 2 thįdebo3/ |
| I-Nom rice-Acc eat-Fut (1Sg) -Cau |
`I1 (was forced to) eat3
rice2 (by someone)’
|
|
Semantically the event is past, but
the grammatical marking is with the immediate future tense suffixes.
|
| (183)
|
/h 1 tap 1 tap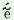 2
thįsyiga3/ 2
thįsyiga3/ |
| I-Nom [A] rice-Acc eat-Cau-Aff |
`I1
caused (someone) to eat3
rice2’
|
|
| (184)
|
/h 1
tap 1
tap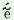 2
thįde3/ 2
thįde3/ |
| I-Nom A/E rice-Acc eat-IF (1Sg) |
`I1 eat3
rice2’
|
|
The agent and the executor cannot
occur together in a surface sentence. If both are to be specified, it is
essential to add an entailment to the sentence.
|
| (185)
|
/h 1
thįsyiga2, nyś3
thįdebo4/ 1
thįsyiga2, nyś3
thįdebo4/ |
| I-Nom eat-Cau you-Nom eat-Cau |
`I1 caused2 you to eat4’
|
|
| The causal suffixes can occur with
only action verbs since the presence of an agent or an executor is
obligatory. |
2.5.3.2.6.
|
Movement : |
|
Mishmi verbs can be inflected for movement. It indicates
that the action represented by the verb is preceded by some movement. The
movement is necessarily directional, in the sense that the movement is
either towards or away from the speaker prior to the event. It is marked by
the suffix /-ge/. The event is always in the past time though tense is not
overtly marked. The morpheme is in complementary distribution with all other
inflexional suffixation.
|
| (186)
|
/h 1 tap 1 tap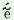 2
thįge3/ 2
thįge3/ |
`I1 went/came (and) ate3
rice2’
|
|
| (187)
|
/h 1
tap 1
tap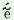 2 thįso3/ 2 thįso3/ |
`I1 ate3 rice2’
|
|
There are some occurrence
restrictions imposed on movement. It occurs with only action verbs. However,
action verbs of directional motion like `go’, `come’, etc., are exceptions
and do not undergo inflexion for movement as the sentences given below
exemplify.
|