/-yą/ when the subject is second
person;
|
| (95) |
/nyś1
į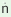 2
hanįyą3/ 2
hanįyą3/ |
| come-DF |
`you1 will come3
hom2’
|
|
| (96) |
/įnč1 jy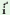 m2
maróyą3/ m2
maróyą3/ |
`you1
shall tell3
the truth2'
|
|
/-b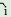 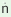 /
and /-biya/ when the subject is third person. These suffixes
are in free variation. /
and /-biya/ when the subject is third person. These suffixes
are in free variation.
|
| (97a) |
/wé1
į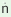 2
bób 2
bób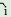 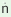 3/ 3/ |
`he1 will go3
home2’
|
|
| (97b) |
/wé1
į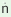 2
bóbiya3/ 2
bóbiya3/ |
| go-DF |
`he1
will go3 home2’
|
|
A different system of tense
distinctions operates for a subset of verbs. The verbs in question, the
cognitive, sensory, existential and ambient states, do not exhibit a four
way tense distinction, but a three way one for past-present-future
apposition without the corresponding continuous aspect inflexion.
|
(v) Past tense is marked by the
suffix /-so/ :
|
| (98) |
/jyimcyanewč1 jy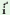 m2
kasąso3/ m2
kasąso3/ |
`Jimchane1
knew3
the truth2’
|
|
| (99) |
/jyimcyanewč1 b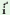 rõy rõy 2
rśgaso3/ 2
rśgaso3/ |
`Jimchane1
loved3
the niaid2’
|
|
| (100) |
/b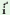 yą yą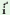 yągõ1
jyįbmalł2 helóso3/ yągõ1
jyįbmalł2 helóso3/ |
`long ago1
Jabmalu2 was happy3’
|
|
(vi) Present tense is marked by
suffixes which are governed by concord restrictions :
|
/-de/ occurs with non-third person
subjects.
|
| (101) |
/h wč1
dįykt wč1
dįykt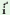 k k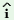 2 kasąde3/ 2 kasąde3/ |
`I1 know3
the Mishmi language2’
|
|
| (102) |
/nyśwč1 é2
m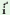 yąą3 rśgade4/ yąą3 rśgade4/ |
`you1
love4
this2 girl3’
|
|
| (103) |
/h wč1 masy wč1 masy
 tyóde2/ tyóde2/ |
`I1
am hungry2’
|
|
| (104) |
/n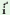 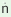 wč1
sy wč1
sy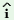 de2/ de2/ |
`we1 are fair2’
|
|
| (105) |
| /įnčwč1 prąde2/ |
`you1 are good2’
|
|
/-yą/ occurs with third person
subjects.
|
| (106) |
/cyįwč1
h 2
įy 2
įy 3 rśgayą4/ 3 rśgayą4/ |
`he1 loves4
my2 daughter3’
|
|
| (107) |
/macy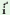 gwč1 thaygayą2/ gwč1 thaygayą2/ |
`the water1
is hot2’
|
|
| (108) |
| /jyimcyanewč1 dłkayą2/ |
`Jimchane1 is sad2’
|
|
The existential verb has a different
tense distribution. The above suffixes occur only
|