It is produced the same way as [c], its
voiceless counterpart, except that the vocal folds come together and vibrate
to produce ‘voice’. The velic is raised to close the nasal passage. |
It occurs initially and medially, before the vowels [i]
[i], and [a] [in a loan word] |
Initial
|
|
|
Medial
|
mōj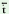 |
‘pumpkin, large in size, one of various kinds’ |
| ōjĭ |
‘size’ |
|
[ch] is the breathed aspirated palatal affricate
|
| It is produced the same way as [c], its
unaspirated counterpart, except that there’s a puff of breath accompanying
it. The vocal folds are kept apart in a state of voicelessness and the velic
raised to close the nasal passage. |
It occurs initially, in a limited number of
words.
|
ch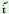 |
‘to hang up on a hook’ |
ch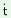 |
‘to insert ring on a finger’ |
ch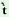 |
‘to knit’ |
| chu |
‘thousand’ |
|
The function load of contrast between [c] and [ch]
is appreciably low.
|
[f] is the breathed labiodental fricative.
|
| It is produced when the
lower lip is drawn up to touch the upper teeth leaving
a constriction open for the air to squeeze through.
It is almost the same as the English [f], in its articulation,
in other words like first, fount etc. The
vocal folds are kept apart in a state of voicelessness
and the velic raised to close the nasal passage. |
It occurs both initially and medially.
|
Initial
|
f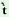 |
‘to cook by putting under ash or an cinders’ |
| fōlā |
‘navel’ |
|
Medial
|
| ķfģ |
‘to dip, dunk, sop, souse’ |
| ōfŭ |
‘lung’ |
|
[v] is the voiced labiodental fricative.
|
| It is produced the same was as [f], its
voiceless counterpart except that the vocal folds come together and vibrate
producing ‘voice’. The velic is raised to close the nasal passage. It is
almost the same, in its articulation, as the English [v] in words like vet,
vice, veal, etc. except for a lesser degree of frication. |
It occurs initially and medially
|
Initial
|
vķpr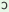 |
‘Venus’ |
|
Medial
|
| ōvō |
‘daughter-in-law’ |
| ōvł |
‘1. Star |
2. planet’ |
|
[ş] is the breathed, retroflex fricative.
|
It is produced when the apex of the tongue is
raised and curled back towards the hard palate, or even more back leaving a
narrow opening for the air to squeeze through. The vocal folds are kept
apart in a state of voicelessness and the velic raised to close the nasal
passage.
|
It occurs initially and medially.
|
Initial
|
| şŏ |
‘to open [as box, door, window, bag etc.]’ |
| şį |
‘to pluck flowers’ |
| şą |
‘to raid’ |
|
Medial
|
|
|
|
It is difficult auditory to tell the voiceless
retroflex fricative from the coarticulated segment of the voiceless trill
and the voiceless glottal fricative symbolized as [hŗ]. Spectrograms,
however, put the issue beyond doubt. Spectrogram 1 below is a display of the accoustics of the voiceless retrofelx fricative in the word [prişi] ‘to
slip’ and spectrogram 2 of the accoustics of the co articulated segment in
the word [kohru] ‘physique’.
|