|
3.9.1. Types of pronouns: |
| |
Lotha
has the following pronouns
1. Personal
2. Demonstrative
3. Interrogative
4. Reflexive
5. Indefinite
|
| |
3.9.1.1.
Personal pronoun :
|
| |
The
system of personal pronoun in Lotha distinguishes for three
persons, two numbers and three genders. Gender distinction
in pronoun takes place only in the third person. However,
this type of gender distinction is maintained only in human
pronouns. In case of animate nouns gender distinction is
made by the gender marker or gender words as explained in
3.5.
|
|
Forms
of Personal Pronouns are as follows : |
|
|
Singular |
plural |
| First Person |
 |

|
| Second Person |
n |
nt
|
Third Person
(Masculine) |
mp |
 nt nt
|
Third Person
(feminine) |
np |
 nt nt
|
|
|
|
|
|
Personal
pronouns whether singular or plural when occur as the subject
of the sentence, nominative or agentive marker -n¡
or -y°
or -n°
is added.
|
|
| Examples |
1.  -n -n |
ótsì |
ts  -là -là
|
I eat rice |
| I-nom |
rice |
eat-present |
|
2.  -n -n |
ótsì |
ts  -là -là
|
we eat rice |
| we-nom |
rice |
eat-present |
|
3.
 -y -y |
sk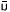 l-ì l-ì |
y -là -là |
I
go to the school |
| I-nom |
school-to |
go-present |
|
4. nt -n -n |
òtsì |
ts  ¡-là ¡-là |
|
| you-nom |
rice |
eat present |
You (as a group) eat the
rice |
5. mp -n -n |
ótsì |
ts  -là -là |
He eats rice |
| he-nom |
rice |
eat-present |
|
6. np -n -n |
ótsì |
ts  -là -là |
She
eats rice |
7.  nt nt -n -n |
ótsì |
ts  -là -là |
|
| they-nom |
rice |
eat-present |
They (as a group) eat rice |
|
|
|
|
|
|
In
case of first person plural form  y y , ,
 is the base for the first perso plural and y
is the base for the first perso plural and y is the nominative marker. In case of
is the nominative marker. In case of  t t , ,
 is the base for the first person plural and t
is the base for the first person plural and t is a quantifier.
is a quantifier. |
|
Examples
|
|
1.  -y -y |
ótsì |
ts  -là -là
|
|
|
we-nom |
rice |
eat-present |
We eat rice |
2.  -t -t -n -n |
ótsì |
ts  ¡-là ¡-là
|
|
|
We-quantifier |
rice |
eat-present |
We (as
a group) eat |
| -nom rice |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In
case of second person pronouns, the singular form is n and plural form is nt
and plural form is nt where t
where t is not a plural marker but a quantifier. n
is not a plural marker but a quantifier. n is the base for second person singular, n
is the base for second person singular, n ,
n ,
n or y
or y are nominative markers that occur when n
are nominative markers that occur when n is the subject of the sentence. In the second person plural
n- can be taken as base and -t
is the subject of the sentence. In the second person plural
n- can be taken as base and -t as quantifier. Third person masculine form is mp
as quantifier. Third person masculine form is mp and feminine form is np
and feminine form is np ,
here, -p ,
here, -p can be taken as base for the third person and m- and n-
as gender markers for the masculine and feminine respectively.
Third person plural form is
can be taken as base for the third person and m- and n-
as gender markers for the masculine and feminine respectively.
Third person plural form is  nt nt where
where  n-
can be taken as base for the third person plural and -t n-
can be taken as base for the third person plural and -t is the quantifier.
is the quantifier.
|
|
|