| j
is a voiced palatal affricate. It has two allophones and j.
The palatal voiced affricate j occurs before front vowels and
the alveolar voiced affricate j occurs elsewhere. However j
freely varies with j before non-front vowels. This phoneme
occurs in the initial and medial positions only. |
| Examples: |
|
|
Phonetic
|
Phonemic
|
|
|
j
|
ji gra gra
|
ji gra gra
|
‘basket’
|
|
|
ji a a
|
ji a a
|
‘spiked
gourd’
|
|
|
 === === l l
|
 === === l l
|
‘prison’
|
|
j~j
juli
|
juli
juli
|
juli
|
‘money
belt’
|
|
|
hamjuk~
|
hamjuk
|
‘daughter-in-law’
|
|
|
hamjuk
|
|
|
|
|
j to~j to~j to to
|
j t t

|
‘all’
|
|
|
|
k is a voiceless velar stop. It occurs in the initial, medial
and final positions. |
| Examples: |
|
Phonetic
|
Phonemic
|
|
|
kami
|
kami
|
‘village’
|
|
|
|
‘front’
|
ku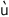 k k
|
ku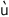 k k
|
‘insect’
|
|
|
|
kh is a voiceless aspirated velar stop. It occurs in the initial
and medial positions. |
| Examples: |
|
Phonetic
|
Phonemic
|
|
|
khum
|
khum
|
‘flower’
|
|
|
 Ekh Ekh k k
|
‘basket
to keep ashes’
|
|
|
| g
is a voiced velar stop. It occurs in the initial and medial positions. |
| Examples: |
|
Phonetic
|
Phonemic
|
|
g 
|
g 
|
‘bear’
|
|
phugo
|
phug
|
‘hole’
|
|
|
| 1.3.1.2.
Fricatives: |
|
s is a voiceless fricative. It freely varies in many examples
with voiceless alveolar aspirated affricate ch before non-front
vowels. It occurs only in the initial and medial positions. Finally
it occurs only in the borrowed words. |
| Examples: |
|
|
Phonetic
|
Phonemic
|
|
|
s
|
si
|
si
|
‘wet’
|
|
|
siyari
|
siyari
|
‘dew’
|
|
|
|
|
‘servant’
|
|
s
~ ch
|
saal~chal
|
sal
|
‘day,
sun’
|
|
|
b sa~b sa~b cha cha
|
b«sa
|
‘child’
|
|
|
b s
~ b s
~ b ch ch
|
b s s
|
‘mongoose’
|
|
|