| 1.3.3.
Tones: |
| In Kokborok, vowels
are pronounced in two ways. Some are pronounced with average pitch
necessary for speaking while the others are pronounced with the pitch
higher than the average. The average pitch is predominant in the words
of this language, and it is referred to as level tone. The other pitch
is called high tone. The high tone in this language occurs with all
the vowels except «. |
| Examples: |
hay hiN hiN
|
‘ginger’
|
|
‘sand’
|
b ra ra
|
‘fence’
|
¸
b ra ra
|
‘keep’
|
|
thµy
|
‘death’
|
¸
thµwy
|
‘blood’
|
ba la la
|
‘change’
|
¸
baÛ la la
|
‘earthquake’
|
|
yasku
|
‘finger
nail’
|
¸
yaskuÛ
|
‘elbow’
|
y N N
|
‘uncle’
|
¸
y ÛN ÛN
|
‘insect’
|
|
|
| 1.4.
General and Distributinal facts about Kokborok sounds: |
| 1.4.1.
Stops and nasals show three-way contrast in terms of point of articulation,
viz., bilabial, alveolar and velar. The stops show another
three-way contrast in terms of manner of articulation, viz., voiceless,
voiced and aspirated. The voiced aspirated series is absent in kokborok.
The alveolar stops freely vary with the dental stops. Only the voiceless
stops occur in the word final position. |
| 1.4.2.
All the consonants are palatalised after /y/.e.g., phaykya
‘came’, paykhya ‘finished’, syty’true’.
The nasals are palatalised completely and become palatal nasals.
e.g., sayn)a
‘bugle’, kayñani 'sow'. |
1.4.3.
Kokborok has altogether six affricates and
two sibilants: [c] [ ]
[j] [ ]
[j] [ ] [ch]
[ ] [ch]
[ h] [s]
[ h] [s]
[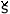 ]. The
palatal affricates [ ]. The
palatal affricates [ ]
and [ ]
and [ ] occur
before front vowels and freely vary with the alveolar ones elsewhere.
The alveolar affricates do not occur before front vowels. The sibilants
[s] and [s&]
freely vary with the aspirated [ch] and [ ] occur
before front vowels and freely vary with the alveolar ones elsewhere.
The alveolar affricates do not occur before front vowels. The sibilants
[s] and [s&]
freely vary with the aspirated [ch] and [ h]
respectively. [s] however does not freely vary with [ch] before front
vowels. There are also a few words in which all the four sounds [s],
[ch], [s&]
and [ h]
respectively. [s] however does not freely vary with [ch] before front
vowels. There are also a few words in which all the four sounds [s],
[ch], [s&]
and [ h]
freely vary with each other (e.g., sa~ h]
freely vary with each other (e.g., sa~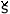 a~cha~ a~cha~ ha
‘child’). ha
‘child’). |
| The
distrubution of affricates and sibilants given above can be analysed
in two ways as given below following the structural model. |
| I.
we may treat the freely varying sounds as units and have the following
phonemes and allophones. |
|
a)
|
/c~ / /
|
[c~ ] ]
[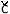 ] ] |
before
non-front vowels
before front vowels
|
|
b)
|
/j~ / /
|
[j~ ],[ ],[ ] ]
|
before
non-front vowels before front vowels
|
|
c)
|
ch/s~/
[s]
|
[s~ch]
|
before
non-front vowels, before front vowels
|
|
d)
|
/s~ch~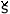 ~ ~ h/ h/
|
|
before
non-front vowels, before front vowels
|
|
|
II.
alternatively, we may choose any four of the freely varying eight
sounds c, ch, j,  , ,
 h, h,  ,
s and ,
s and 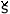 as
the phonemes. as
the phonemes. |