| Examples: |
|
Phonetic
|
Phonemic
|
|
|
thµk
|
yhµk
|
‘louse’
|
sµ
|
sµ
|
‘ask’
|
|
tµy
|
tµy
|
‘water’
|
|
bagµy
|
bagµy
|
‘for,
because of’
|
|
|
kµ µN µN
|
‘bright’
|
|
|
|
« is a mid central unrounded
vowel and is slightly retracted towards the back. It occurs in polysyllabic
words and is always followed by a or
another «
in the next syllable |
| Examples: |
|
Phonetic
|
Phonemic
|
|
k rak rak
|
k rak rak
|
‘hard’
|
ra b b taN taN
|
|
‘necklace’
|
|
|
|
‘active’
|
|
|
| a is a low
central unrounded vowel. It occurs in all the three positions and
shows a very high frequency of occurrence. |
| Examples |
|
Phonetic
Phonemic
|
|
|
|
amiN
N
|
‘cat’
|
‘cat’
|
|
tal
|
tal
|
‘moon,
month’
|
|
thapa
|
thapa
|
‘oven’
|
|
|
| 1.3.2.3.Back
Vowels: |
| u has two allophones:
(1)u the high back rounded vowel, occurs in the final position or
after a bilabial; (2) the lower-high back rounded vowel u
occurs elsewhere. |
| Examples: |
|
|
Phonetic
|
Phonemic
|
|
|
u
|
puthi
|
puthi
|
‘book’
|
|
|
 ibuk ibuk |
 ibuk ibuk
|
‘snake’
|
|
|
philigu
|
philigu
|
‘lightning’
|
|
u
|
Uro
|
ur
|
‘three’
|
|
|
Ura
|
ura
|
‘basket’
|
|
|
|
has two allophones:
(1) the mid back rounded vowel o occurs
either in the final position or after y; (2) the higher-low
back rounded vowel
occurs else where. |
| Examples: |
|
|
Phonetic
|
Phonemic
|
|
|
0
|
soidi
|
s ydi ydi
|
‘sign’
|
|
|
koili
|
k yli yli
|
‘nose-ring’
|
|
|
i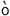 N N
|
y N N
|
‘insect’
|
|
|
r mo mo
|
r m m
|
‘pestle’
|
|
c
|
|
Ûg«naN
|
‘pregnant’
|
|
|
|
|
‘all’
|
|
|
|
p  a a
|
‘load’
|
|
|
b r r k k
|
b r r k k
|
‘man’
|
|
|