It
is not necessary that the imperative auxiliary occurs
just after the verb; an adverbs also could occur in
between. For example : |
/tíem
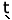 há
r há
r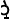 h/ h/ |
‘read
well’ |
/th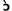
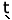 há
r há
r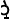 h/ h/ |
‘do
well’ |
/fè
vát r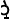 h/ h/ |
‘go
immediately’ |
|
|
|
|
The
subjunctive Mood, whenever necessary, is realised by
using auxiliary /cun/ post positionally after simple
present tense verb forms. For example : |
/ká
th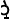 :
cùn/ :
cùn/ |
‘if
I do’ |
| /í
hrìl cùn/ |
‘if
you tell’ |
| /à
zá:l cún/ |
‘if
he lies down’ |
|
|
|
|
The
past conditional, wherever necessary, is realised by
using a set of two auxiliaries as post positions after
simple present tense verb forms. These two auxiliaries
are /di /
and /bah/, of which the former is a post position marking
future. /
and /bah/, of which the former is a post position marking
future. |
/ká
th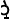 :
dí :
dí bàh/
bàh/ |
‘I
would have done’ |
/ì
hú dì
dì bàh/
bàh/ |
‘you
would have come’ |
/á
thàt dí bàh/
bàh/ |
‘he/she
would have killed’ |
|
|
|
Past
conditional can be further emphasised by the addition
of more past indicating words like /ta/ and /dai/ indicating
possible completion of actions- For examples: |
/ká
th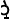 :
tà d :
tà d bàh/
bàh/ |
‘I
would have had done’ |
/ká
th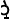 :
dài tà dí :
dài tà dí bàh/
bàh/ |
/I
would have had (completed) done’ |
/ká
zóu tà dí bàh/
bàh/ |
‘I
would have had completed’ |
/kà
zóu dài tà dí bàh/
bàh/ |
‘I
would have had (completed) completed; literally,
I would have completed the completion’ |
/ì
hú tà dí
tà dí bàh/
bàh/ |
‘you
would have had come’ |
/ì
hú dài tà dí
dài tà dí bàh/
bàh/ |
‘you
would have had (already) come’ |
/á
thàt tà dí bàh/
bàh/ |
‘he/she
would have had killed’ |
/á
thát dài tà dí bàh/
bàh/ |
‘he/she
would have had (finished) killing’ |
|
|
|
|
The
optative mood, wherever necessary, is realised by using
a pair of auxiliaries such as /èl/
and thèi/ after simple present tense verb forms. For
example: |
/ká
th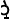 :
èl thèi/ :
èl thèi/ |
‘I
may do’ |
/ì
hú èl thèi/
èl thèi/ |
‘you
may come’ |
| /á
hríl èl thèi/ |
‘he/she
may tell’ |
|
|
|
For
further emphasis, the same past indicating words /ta/
and /dai/ may be used. Example: |
/ká
th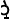 :
tá èl thèi/ :
tá èl thèi/ |
‘I
may have done’ |
/ká
th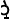 :
tá dài èl thèi/ :
tá dài èl thèi/ |
‘I
may have had done’ |
|
|
|
|
The
non-finite verbal constructions in Hmar could be discussed
under two heads:
a. Infinitives, and
b. verbal participials
Both the categories are insensitive to person, number,
gender, tense and mood. |